Sales Glossary for Sales Terminologies
Sales Glossary (A to Z)
If you’re starting in B2B sales or a first-time manager at a company that is new to B2B sales, then this glossary will help you grasp basic terms and concepts of sales. This sales glossary is a companion piece to the larger list of B2B sales terms (which covers words, phrases, and acronyms). Basically, it serves to break down those commonly used sales terms into a simple language. The idea behind this is that by the end, not only will the sales professional fully understand what they mean, but also find an ideal example of how to use it when on a sales call with a client.
−A−
ABC
ABC is an acronym for “always be closing”. It is an ancient sales strategy embedded in the idea that every step a salesman takes throughout his sales journey should lead to closing a deal.
Example: Let’s suppose a sales guy generates leads through research and then reaches the potential customers via call or email. After that, he nurtures the clients by telling them why they need the product. Next to it, he follow-ups regularly, and finally, they are converted into paying customers. All these basic steps, such as lead generation, nurturing, and follow-ups taken by a salesperson, are the stages of the ABC approach.
Above-the-Fold
Above-the-Fold is a marketing term that refers to the portion of the text that appears on the top half of a website, landing page, or printed publication.
It’s usually the place where the most significant information is given so that if a website visitor or a prospect doesn’t scroll down, you will still be able to catch their attention and make them take action.
Example: When you visit the landing page of EasyLeadz’s website, you will see above-the-fold content, which is written as “Find Phone Numbers of top management In One Click”. This will persuade the prospects to install the tool, Mr.E by EasyLeadz to find the contact details of the C-level executives.
AB Testing
AB Testing is an experiment between two variants, named A and B to measure and compare the market response to each variant. Usually, the companies perform AB testing to find out which approach attracts more customers. It is also known as Split testing.
Example: You can compare two different web pages of a website about the same product to test which page generates more leads. You can also perform AB testing on Facebook posts. You can test with two different posts to compare which post has more engagement, reach, likes, or comments.
Account
Account means a record of all the primary and background information about a customer’s contact details, preferences, and purchase history with your company. An account is created when a customer purchases for the first time from your company.
Example: Companies have Cash accounts to record every transaction. Similarly, they have Asset accounts to keep a record of the debit balance.
Account-Based Everything
Account-based Everything (ABE) or Account-based Revenue (ABR) is a support system in which companies plan and monitor the activities per targeted customer account by providing full coordination of customized care and management to them.
In this, the various segments of a company (like sales, marketing, product development, and finance) work towards fulfilling the requirements of high-value client accounts. This process is integrated into the lifecycle of the client experience from lead generation to after-sales support.
Example: A company X trying to sell expensive software. It would make no sense if the company targets every small or mid-size company. In this case, the accounts (companies) who actually need the software and can afford it would be worth to reach for a successful closure. Further, Company X can reach them by making a plan or running campaigns for the next 3 or 6 months.
Account-Based Marketing (ABM)
Account-Based Marketing (ABM) is a highly focused and personalized strategy in which the most potential customer accounts of a company are targeted with special promotions, sales, and marketing strategies.
Example: EasyLeadz targeted companies (especially the decision-makers in those companies) that have more than 500 employees. This specific targeting by implementing ABM helped it to increase its pipeline growth faster and also achieved a higher win rate.
Account-Based Selling (ABS)
Account-Based Selling (ABS) or Account-Based Sales Development (ABSD) is a comprehensive, hyper-personalized B2B sales strategy in which the most valuable business accounts of a company are segregated into groups and targeted with exclusive deals, agreements, and specialized services.
This B2B selling framework follows the concept to take the 1-on-1 approach to the higher level, by targeting an entire account instead of single contacts and assigning an entire sales team towards targeting various decision-makers within an organization. The departments that are the most integral part of account-based selling are sales, marketing, and customer success.
Example: In B2B marketing, usually there are few people who make the purchase decision. These are 5 to 7 decision-makers in a single organization. If you target or manage these high-value accounts for a specific period of time, you will be able to close a deal. This is the tactic for ABS.
Account Development Representative (ADR)
An account development representative (ADR) is a sales specialist who identifies potential customers, develops sales strategies, maintains a solid understanding of the current market, and participates in other activities that help an organization fulfill its sales goals.
More so, an ADR also focuses on generating quality leads, increasing conversion rates, and client engagement. The ultimate purpose of hiring an ADR is to allow other salespersons to focus on closing sales.
Example: We all know that the head of the family (who is usually a father) manages all the finances to ensure the maximum outcome. Similarly, an ADR acts in the same manner by handling the accounts of existing customers and developing engaging sales strategies to generate more potential leads.
Account Executive (AE)
An account executive (AE) is a sales executive who has a core responsibility for managing one or more customer accounts (called a portfolio) and building relationships with quality leads for a company.
He is also responsible for nurturing these accounts from the portfolio by presenting solutions, uncovering their pain points, doing demos, and negotiating contracts. He communicates with both the prospects and the existing customers to know their concerns.
He requires to have a huge knowledge of the company’s value proposition so that they can relate it to the requirements of a particular customer. An AE of a company takes over the sales process from an ADR and works towards closing a deal by representing that company or product and also answering the challenging questions gracefully.
Example: In a family, the mother just like the father contributes in managing the finances and finding ways to increase income. So, an AE does the same thing by helping an ADR but with the mindset of driving more sales for the organization.
Accounts Payable
Accounts Payable means an accounting entry representing the amount of short-term balance that your company borrows from its vendors, suppliers, and other service providers. This amount is reflected on a company’s balance sheet in the form of liabilities.
Example: Let’s suppose Company A has to deliver its products to its consumers. For this purpose, it will require a transportation service, and to avail that service, it has to pay some specific amount of money, that money is considered as “Accounts Payable”. Similarly, there are other expenses too like logistics, raw materials, licensing, etc. for which a company has to pay.
Accounts Receivable
Accounts Receivable means a certain amount of money yet to be received from your customers for the goods or services provided by your company.
Example: An electric company that provides electricity to its clients and bills them after they received it. The electric company keeps recording accounts receivable for unpaid invoices as it waits for its clients to pay their bills
Accredited Investor
An accredited investor is a person who has privileged status and legally makes $200,000 or more in annual take-home income ($300,000 with a spouse) or if they have a total net worth of $1M excluding their home’s worth.
Example: Accredited Investors include banks, brokers, trusts, insurance companies, and high net-worth individuals.
Adoption Process
The adoption process is another term for the buying process that introduces the customer to the product and represents their final decision regarding it (approval or rejection). This process does not lead towards closing a sale.
Example: Let’s consider a company launches its product A and informs the prospects via newsletter. Now, the seller will contact them to know whether they are interested to buy the product or not.
Advantage
Advantage is the positive attribute of a product or a tool that does not require an emotional appeal.
Example: A laptop is better than a PC for a working professional who travels on a frequent basis.
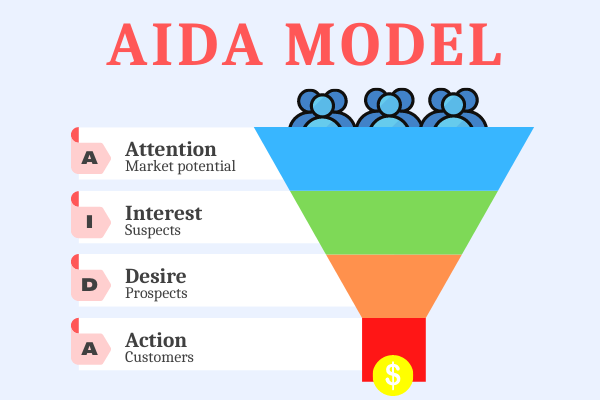
AIDA
AIDA is a Sales acronym that stands for “Attention/Awareness, Interest, Desire, Action”. These four stages are the integral attributes of the basic sales funnel. The AIDA model represents what a potential client goes through in the buying process. It also describes how marketers have mapped the initial process.
Example: Suppose EasyLeadz – a B2B contact data provider company wants to skyrocket its sales. Then the AIDA approach for it to boost sales is like this:
Attention: If you are looking for the contact numbers of decision-makers then you have landed at the right place as Mr. E by EasyLeadz is here to provide you the contact numbers of decision-makers.
Interest: Business directories and local search engines charge a lot of money for business listings and contact details.
Desire: But with Mr. E, it is completely affordable. And if you compare it with any other websites, then Mr. E provides more data fields like direct phone number, email ID, company profile, etc.
Action: Contact us here to get more information about our product.
Amortization
Amortization means paying off debt through a fixed scheduled payment plan.
Example: A car loan or a mortgage via installment payments.
Analytical CRM
CRM means Customer Relationship Management. Analytical CRM is a technology-based system that enables marketers to handle customer accounts, keep up with leads, track client behavior and adapt processes based on analytical data.
Example: Suppose you want to see the sales of a particular product for a specific time period, then you can use an analytical CRM. Salesforce, HubSpot, and Zoho are some common examples of an analytical CRM system.
Analytics
Analytics is the active study of various kinds of data that is collected over time about clients (their behavior, trends, and purchases) to find informative patterns, convert these into insights and also intend to improve business processes, and plan opportunities.
Example: With the help of Analytics, you will be able to analyze the trends, e.g, Google Analytics, a web analytics service provided by Google to analyze or track the website traffic. Similarly, you can perform customer analysis that shows what percentage of male customers in their 20s are more likely to buy a certain product at price A in comparison with price B.
Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR)
Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) is a metric representing the annual subscription revenue (contractual-based, recurrent revenue) of a subscription-based company or a SaaS. It is the money that a company makes from its subscribers during a year. It is really useful for long-term planning.
Example: If a company buys an annual subscription for Rs.1,00,000, then the ARR will be Rs.1,00,000 for each year. ARR is a predicted revenue and can be calculated for every year.
Applicant Tracking System (ATS)
Applicant Tracking System (ATS) is software used by HR (Human Resources) departments to follow the full cycle of recruitment, from job application to the final offer letter.
Example: Oracle Taleo is an ATS to manage all the hiring needs and acts as a data bank for all the recruitment processes.
Application Program Interface (API)
An Application Program Interface (API) is an accessible technical framework that makes it possible to pass information between two websites, apps, or applications. It is a software interface that allows two software to interact and communicate with each other without any user intervention.
Example: If we want to find the contact number of a person using EasyLeadz, then with API we can send the name of the person as an input to the server and get the contact number in return as an output.
Appointments Set
Appointments Set is a term used to schedule the number of (in-person or phone) appointments that a salesperson has with potential leads.
Example: Our sales representatives at EasyLeadz use Calendly to set a date (and time) for their prospects to give a demo about the tool, Mr. E. That date which they will set is an appointment set.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the ability of a digital computer or a robot controlled by a computer to perform tasks that are usually done by human beings.
It is a system or network of computers, processes, and software that simulates human processing intelligence by programming it to interpret and process external data sets and learn from them. AI is used in businesses to boost productivity, improve various processes, perform analysis on large data volumes, and hence make better decisions.
Example: The real-time examples of artificial intelligence (AI) are Alexa and Siri, digital voice assistants.
Autodialer
Autodialer is a system automated to dial random contact numbers from a database and programmed to leave messages on answering machines and request information.
Example: Dialpad, CallHub, Five9, ChaseData, Talkdesk, and Voxco are some autodialer software.
Autoklose
Autoklose is a sales automation platform with a plethora of beneficial features like a template analyzer and email campaign manager that can assist you in closing more sales.
Example: You can click here to use the sales automation tool, Autoklose, which helps sales professionals to close more deals at a great speed.
Autoresponder
Autoresponder is a computer program that automatically sends messages to new users after they subscribe or takes action. These automated messages can be very simple or complex, and various triggers can activate them.
Example: We at EasyLeadz send a welcome email the minute after they install the tool, Mr. E.
Average Contract Value (ACV)
Average Contract Value (ACV) is the average annualized revenue a company earns from a single customer contract within a given time period. If the same metric is calculated per year, it is known as Annual Contract Value (ACV), otherwise, Average Purchase Value (APV) when the revenue earned is not subscription-based.
Example: If you had a client who signed a 2-year contract for Rs. 24,000, then your ACV is Rs.12,000.
Average Dollar per sale (ADPS)
Average Dollar per sale (ADPS) is a formula in which the marketers divide the total dollar amount of sales over a chosen time period by the number of customers.
Example: Let’s say you have generated $ 4,00,000 of revenue by selling your product to 200 customers for the month. Now divide the revenue generated in that month by the number of customers you sold to during that month. The result that you will get is your Average Dollar per Sales. In this scenario, the ADPS will be $ 2,000 per customer.
Average Sale/Selling Price
Average Sale/Selling Price (ASP) is a term that refers to the average price of a product or a group of products/services in a market.
Example: Let’s say you have the prices of newly built houses (near your locality) in the last 10 days. Now you add up the seven different prices and then divide their sum by seven (the number of prices). Then, the result which you will get is the average selling price for those houses.
-B-
B2B
B2B is a Business-to-Business sales model in which one business (or a company) markets and sells solutions to another business (another company).
Example: EasyLeadz is a B2B company that deals with other businesses (companies) to provide a B2B solution for getting the contact details of the top management in a single click.
B2C
B2C is a Business-to-Consumer sales model in which a business (company) markets and sells products or services directly to the consumers.
Example: Flipkart, Amazon, and Meesho are the B2C companies that directly deal with the consumers. Even a grocery store near your locality is a B2C segment as it directly sells to the customers.
B2C2B
B2C2B is a Business-to-Consumer-to-Business, sales model in which a business (company) targets an employee (acts as a consumer) from another business in order to acquire that business as a client.
Example: Some good examples of B2C2B sales models are Gmail, Hubspot, Dropbox, LinkedIn, and Slack.
BAB Formula
BAB formula is a Before-after-bridge storytelling formula that is used in sales, marketing, and advertising to show your clients their pain points before telling them about your solution and how things will get better after using your solution. This strategy is really helpful in cold emailing.
Example: Let’s say EasyLeadz wants to boost its sales by adopting a BAB formula, then the approach would be like this:
Before: Finding contact information of decision-makers has always been a tedious task. If you don’t have the right connections in your company or industry, getting the contact details of someone becomes near impossible.
After: But now with Mr. E, you can quickly find the contact details (phone numbers and email addresses) of the decision-makers across the worldwide.
Bridge: Mr. E by EasyLeadz is a simple yet powerful tool to quickly find the contact details of anyone in your industry and at any company.
Back-out
Back-out is a stage when a client backs out from the sales process or stops the process of purchasing something.
Example: A customer is about to buy a laptop from Flipkart but he denies making a purchase because he gets a better deal for the same laptop on Amazon.
Bad Leads
Bad leads are the potential customers that are not likely to convert into paying customers. A skilled sales representative recognizes bad leads at the early stage of the sales process to avoid wastage of time.
Example: Usually the bad leads are the clients who are just inquiring about the product or service but not really interested in purchasing it.
BANT Framework
BANT stands for Budget, Authority, Need, Timeline. A BANT framework is a sales framework used by sales representatives or sales leaders for lead qualification. The four elements of this framework are there to determine whether a potential client has the budget, authority, actual need, and right timeline to buy what they are selling.
Example: Suppose a salesperson implementing a BANT framework for a particular lead, in which he will first examine the lead’s budget. If the price of the product or service meets with the lead’s budget, then only that salesperson will proceed further. Now he will check, “Does the lead have the decision-making authority?” If yes, he will move further to figure out the business needs of the lead and also find a time frame for which the solution will be implemented.
Base Salary
A base salary is an agreed-upon amount of payment or a fixed salary that an employee received without including bonuses or commission.
Example: Let’s suppose an employee receives a fixed salary of Rs. 20,000, an incentive of Rs. 5,000 and medical insurance of Rs.1000 every month. In this case, the amount of Rs. 20,000 is the base salary of that employee.
Baseline
Baseline means an established minimum level or initial point used to perform further measurements or comparisons for the purpose of analysis, forecasting, strategy formulation, and performance improvement.
Example: Suppose company X wants to examine the success of a product. Now it can use the number of units (of that product) sold during the first month as a baseline against which upcoming monthly sales will be examined.
BASHO Email
A BASHO email is a personalized B2B email that mostly targets the decision-makers with the purpose of getting a first phone call with them.
Example: A personalized email written after conducting detailed research with a catchy subject line and single CTA which add value for your prospect is an example of BASHO email.
Beating Objections
Beating Objections means tackling the customer’s issues or concerns so that they will be able to decide on buying. It is commonly known as “overcoming rejections”.
Example: Usually, after taking a demo of the product, few prospects say, “I really like the product but it is quite expensive” or “I don’t think this product will help me in any way”. So, these barriers which stop them to purchase the product are considered as “Beating Objections” for the sales representative.
Bell-Shaped Curve
Bell-Shaped Curve is a visual demonstration used to measure and examine the performance of the employees.
Example: A pictorial representation (or a graph) in the form of bell curve that shows the ranking of every employee working in company X by categorizing them into a top performer, average performer, and poor performer, based on their performance for a certain period of time.
Benefit
The benefit is the value that a product or service provides to a consumer. It is different from features, and a sales representative should do selling based on the benefits.
Example: When a client of EasyLeadz uses its tool Mr E to get the phone numbers of top management, then the tool also provides email Ids of the professionals for free. So, getting those email Ids is a benefit for the clients of EasyLeadz.
Big Data
Big Data is a huge, diverse collection of data that consists of structured, partially structured, and unstructured data, that can be further processed and analyzed to extract useful information.
Example: The data stored by the different sectors such as Government, Healthcare, Transportation, Education, Banking, Cybersecurity, etc. are some examples of Big Data.
Blacklisting
Blacklisting is the action of blocking an individual, a company or messages (from unauthorized senders by an ESP, ISP, organization, or an individual recipient) by reputed organizations or the government for doing something wrong.
Example: G.Durga Prasad, Rajahmundry Rural, Contractor has been blacklisted from 25th of August, 2020 to 24th of August, 2022 by the government of Andhra Pradesh against the allegation of irregularities happened while selecting the labour.
Bluebird Sales
A bluebird sale is an unexpected sale opportunity that came apparently from nowhere.
Example: Let’s say a company X is getting around 8 to 10 sales during the end of the financial year just through the website itself. Then that sales are the bluebird sales of the company.
Bonus
A bonus is an extra compensation or an additional gift given in addition to the base salary as a reward for excellent performance.
Example: Let’s say a company X is offering a fully sponsored Goa trip to all its employees on generating double revenue. So, that trip is a bonus for all the employees.
Bookings
Bookings are the net dollar amount of new contracts signed, e.g. ACV or TCV.
Example: Suppose someone makes a booking of a room in hotel A. So, for that hotel, the booking is committed or won sale.
Bottom of the Funnel (BOFU)
The bottom of the funnel is the last stage of the sales funnel in which the potential customers are about to become paying customers. This is the point of closing a deal.
Example: Imagine a sales rep approaching 100 prospects in a month. Among those, only 40 prospects are ready to take the demo. After taking the demo, only 5 potential leads become ready to purchase the product. These 5 prospects are at the bottom of the sale funnel and are just a step away from closing a deal.
Bounce-Back Coupon Offer
A bounce-back coupon offer is a coupon that a customer receives after purchasing something. This is to attract the customer to “bounce back”, or purchase more in the given time period.
Example: Let’s imagine you order a pizza from the Dominos and on that order, you have received a voucher of Rs.1000 which you will be able to avail on your next order. That voucher is a bounce-back coupon offer to attract clients.
Bounce Rate
A bounce rate is a metric used to measure the percentage of website visitors who leave the website without taking any other action like visiting the second page, clicking an internal link, or on a CTA (call-to-action).
Example: Let’s say that on the homepage of EasyLeadz’s website, there are 25,000 daily visitors. Among them, 1000 are those visitors who are leaving the website without taking any further action such as visiting a second page, buying the tool, or reading a blog. So, the bounce rate of EasyLeadz’s homepage would be 4%.
Brag Book
Brag Book is a portfolio of a sales representative that includes reviews, testimonials, success stories, and case studies received from happy clients. A sales professional uses his brag book to show how the existing clients benefited from their products or services.
Example: An updated resume of a sales representative including his goals, achieved recognition, awards, milestones, his clients’ reviews, or testimonials.
Bulk Email
Bulk email means sending an email message to a large number of people at one time.
Example: Sendinblue, Amazon SES, Elastic Email, Send Grid, and Mailjet are some common examples for sending bulk emails.
Business Development Representative (BDR)
A business development representative (BDR) or sales development representative (SDR) is a skilled sales professional who focuses on attracting new business prospects, building high-value relationships with customers, and regenerating the sales pipeline with new quality leads for account executives.
Example: Let’s assume a company X wants to expand its business in city A. Now, the company will hire a BDR in that city who would be responsible to accelerate sales growth, develop engaging strategies, and expand the business.
Business Intelligence (BI)
Business Intelligence is the interpretation of primary data, information, and analytics to generate ideas, or to make product and market-based decisions.
Example: Datapine, MicroStrategy, SAS Business Intelligence, Yellowfin BI, and QlikSense are some common examples of Business Intelligence tools.
Buy-Line
Buy-Line is a line on a virtual map that represents the chances of converting a lead into a sale based on their emotional and intellectual engagement. According to it, if a potential customer is below the line, they most probably will not buy what you sell.
Example: Imagine a straight line dividing the graph area into two halves where the X-axis represents “Time” and the Y-axis represents the “Likelihood of Purchase”. That straight line is a buy line, if the prospect is above the buy line, it means he will buy the product. But, if the prospect is below the buy line, then the chances of buying the product will fall.
Buyer
A buyer is an individual person or organizational entity that buys a product or service.
Example: When you visit a local grocery store to buy something, at that time, you are a buyer for the store owner.
Buyer Behavior
Buyer behavior is the customer’s behavior pattern during the buying process. It is normally influenced by their requirements, desires, aspirations, roles, social and cultural environment.
Example: Buying without giving a forethought, buying expensive products, or even purchasing something by taking lots of time before making a purchase decision, all these are buyer’s behavioral patterns or buyer behavior.
Buyer Persona
A buyer persona is a virtual profile of your potential customer, created via market research and real data based on existing customers. This persona is useful for the marketers to find their target audience and qualify leads.
Example: Let’s say you visit a local mobile store to purchase a smartphone. When you have bought it, the owner of the store will note down your name, age, phone number, and address. All these details such as name, age, contact number, email Id, and address of buyer are part of the buyer persona.
Buyer’s Journey
The buyer’s journey is the process that follows a buyer’s progression throughout the sales journey, starting with the research phase and ending up with a purchase decision.
Example: Imagine you have seen an offer of a 50% discount on purchasing a laptop at XYZ shop. In this way, you become aware of the offer for a particular product. Now, you visit the shop to buy it and there are various models of it. You will start considering which suits you the best. Then you will make your final decision to buy it. The journey from becoming aware of the product to make the purchase decision is your buyer’s journey.
Buyer’s Remorse
Buyer’s remorse is a sense of guilt or anxiety that a consumer feels after making a purchase and desires to return or cancel it.
Example: Let’s assume that you have purchased a smartphone from a local mobile store and after using it for few days, it starts hanging. Now, you will feel guilty about purchasing it. That guilt is your buyer’s remorse.
Buying Atmosphere
Buying atmosphere is defined as the continuous efforts made by the sales professional to create an ideal environment so that a lead can be converted into a sale.
Example: Let’s imagine a sales representative from EasyLeadz generates some leads, among them he finds a quality lead. Now he will reach the prospect via call or mail. If he receives a good response from the prospect, then he will make more efforts such as taking his regular follow-ups and keep tracking his buying process until he becomes a paying customer.
Buying Criteria
Buying criteria is all the complete information about the product that a customer requires to purchase it.
Example: Suppose you need a laptop of Dell company, which has i7 generation and 8GB Ram. Now, these requirements set by you are buying criteria for purchasing a laptop.
Buying Intent
Buying intent is a tactic used to determine the probability that a prospect or an organization will buy a product or service. It is concluded from behavioral patterns like media consumption, online browsing, or document downloads.
Example: Suppose you visit the Flipkart website, and search for a certain product. Now, Flipkart advertises the same product to you even when you are using other websites. So, advertising the product on the other platforms is the buying intent for a buyer to make a purchase of the product.
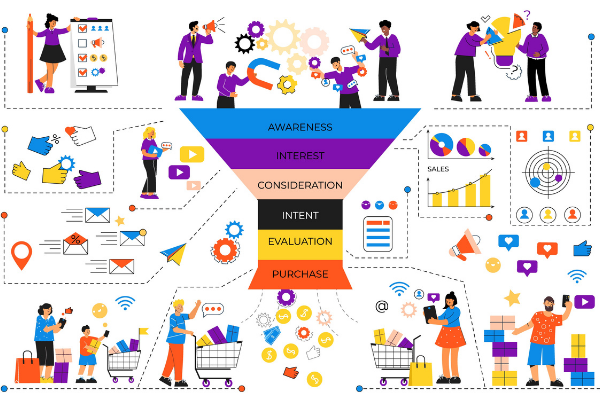
Buying Process/Buying Cycle
The buying process or cycle has various stages that a potential buyer experiences on their journey of buying a product or finding a solution. The buying process has three stages:
1. Awareness: The customer becomes aware of their problem and looks for the solution.
2. Consideration: The customer starts researching to find ways to resolve their problems and considers the possible options.
3. Decision: The customer selects the best solution and makes the purchasing decision.
Example: Let’s assume you have seen a great offer on Mr. E’s annual plans on the homepage of EasyLeadz. Now, you will call the sales rep of EasyLeadz to inquire about the offer and find there are various annual plans with different features. You will start considering which plan you really require as per your business need. Then you will make your purchase decision. The process from becoming aware of an offer to taking the purchase decision is the buying process.
Buying Signal
Buying Signal is a sign by the buyer through verbal or non-verbal communication that shows he/she wants to make a purchase, for example signing up for a free trial. Catching up on these kinds of signals can help sales professionals to better focus on the customers who are giving more buying signals.
Example: Let’s consider you find a great deal of Mr. E bonus credits from EasyLeadz on LinkedIn. Now, you will reach them to inquire more about the offer. So, whatever the action you will take to reach them for inquiring is the buying signal for the sales representatives of the EasyLeadz.
-C-
Call For Proposal
Call for Proposal is the process in which a business asks other companies to sell their product or service in the market.
Example: Suppose there is a wholesale clothing shop A in a city, that will send a call for a proposal to the retail clothing shops to sell their clothing items to the consumers.
Call-Back
Call-back is a way to take follow up of your customers by contacting them repeatedly after a specific time period to know how much they are interested in your product or service or if any decision has been taken towards purchasing it.
Example: Imagine you are a salesperson who is doing cold calling for selling. Now, you call a prospect who shows a bit of interest but is not ready for immediate purchase. Then, you will call back him after 1-2 weeks to know whether he is ready to purchase now or later.
Call-In
Call-In means when a prospect calls to make inquiries about a product, service, or company.
Example: An example of a Call-In is when you make a call to inquire about the latest offer from the company, like an existing customer of EasyLeadz calls on the helpline number to inquire about the offers on the Mr. E bonus credits.
Call-to-Action (CTA)
Call-to-Action is a marketing term. It is a piece of content that encourage potential customers to take an action by clicking on that content. Mostly CTA is used in offers, emails, websites, and on landing pages, for example, “Register for the Webinar”, “Subscribe for our newsletter”, and “Get this offer”.
Example: When you visit the homepage of EasyLeadz, you will find buttons such as “Install Tool”, and “Watch Demo”, these buttons are CTA buttons that will encourage the prospects to install the tool or watch the demo of it.
Calls
Calls can be defined as the process in which one of the members of the sales team contacts a lead either via phone call or in person.
Example: You usually receive calls from the sales representatives of the Telecomm companies to upgrade your plan.
Cap Draw
Cap draw is the maximum limit of the amount that an employee is allowed to take against their salary. The limit that they can take will be considered as an advance payment to the employee.
Example: Imagine your company allows you to take Rs.50,000 per year from it whenever you require it in an emergency. So, that amount is a cap draw for you and you cannot take more than Rs.50,000 from the company.
Cancellation Prevention
Cancellation prevention means taking mandatory precautions to prevent buyer’s remorse.
Example: Let’s suppose you sell bulbs to the consumers, and to avoid buyer’s remorse you ensure that none of the bulbs is defective. That step of ensuring that bulbs are not defective is an act of cancellation prevention.
Cash Collection
Cash Collection is the process of setting up a particular system or various systems through which payment will be made for a product or service.
Example: Cash, drafts, cheques, and payment gateways for receiving the payment from the customers are some examples of cash collection.
Cash Flow
Cash flow is defined as the net amount of money being transferred in and out of a company over some time for operational activities.
Example: Suppose a company X pays out the amount of Rs. 50,000 to avail the transportation service for delivering goods. That amount will be considered as the cash flow outside the company.
Challenger Sales Model
The challenger sales model is a sales framework that uses a unique approach for selling in which the customers are “challenged” out of their comfort zone to purchase a product or service.
Example: Let’s see this conversation between a sales representative and a client to understand the Challenger Sale Model.
*Sales Rep: Hello, Am I speaking to Mr. Rahul from ABC company? *Rahul: Yes, this is Rahul. *Sales Rep: Hi Rahul, I am from EasyLeadz. I guess you are looking for contact data of the HR department. *Rahul: Yes, actually I need it to reach out to all the HRs in India. *Sales Rep: Sure, but can you tell me more about your business? *Rahul: Yes, my company is tech-based, and recently we have launched an HR software that manages all the records of recruitment processes in a very simple way. That’s why we only want to target the HR department. *Sales Rep: Alright, you need software that can provide you the direct phone numbers of all the HRs across the nation. *Rahul: Exactly. But, how can I get that? *Sales Rep: We believe Mr. E by EasyLeadz would be the perfect fit for your company as it provides you the direct phone numbers as well as email Ids of the HRs with 100% accuracy. *Rahul: Great! It sounds interesting. Thanks for solving my problem. *Sales Rep: You’re welcome, Rahul. You can visit the official website of EasyLeadz to purchase the tool.
Champion/Challenger Test:
The champion/challenger test is a testing method that determines the best marketing strategy to follow. The champion refers to the current product or approach whereas the Challenger means new or proposed ways to sell the product.
Example: Champion/Challenger test is similar to AB testing. Let’s assume you have launched a new product and started running a marketing campaign X. Now, after one week, you again run another marketing campaign Y for the same product just to know which marketing campaign will provide better results. So, in this case, the former marketing campaign X is the champion and the later marketing campaign Y is the challenger for X.
Channel Partner
Channel Partner is a person or an organization that provides products or services on the behalf of a vendor through co-branding.
Example: Distributors and resellers are usually channel partners.
Channel Sales
Channel sales refer to the process of segmenting your sales force into different groups that run various distribution channels to sell a product or service.
Example: A perfect example of a company that uses channel sales is PepsiCo. You cannot purchase Pepsi from the company’s website. Instead, you need to purchase it from a third-party vendor such as a grocery store, a food outlet, or another sales channel.
Churn
Churn is a term that represents the percentage of clients who cancel a product or service within a given time period.
Example: Imagine, your company has 1,000 total customers in March and among them, 100 customers stopped buying products from you. So, the churn for that month would be 10%.
Churn Rate
Churn rate is a formula that determines the rate of customers who cancel a product or service. It is calculated by dividing the number of clients you lost by the number you had at the beginning of the given time period.
Example: Let’s assume company A had 1000 clients at the beginning of February but at the end of it there were only 800 clients. Now, the monthly churn rate would be 20% (200/1000*100 = 20%).
Claw-back
Claw-back is defined as taking back the money (in the form of benefits) that has already been paid out to employees.
Example: Public banks can claw back pension payments if there is any proof of fraud by the pensioner.
C-Level/C-Suite Executives
C-Level or C-Suite executives are the high-ranking executives in a company or an organization.
Example: CEO (Chief Executive Officer), COO (Chief Operating Officer), CTO (Chief Technical Officer), CFO (Cheif Financial Officer), or CIO (Cheif Information Officer).
Click-Through Rate (CTR)
Click-Through Rate (CTR) is defined as the percentage of the prospects who clicks on a link or an ad. It is calculated as the number of clicks on a link divided by the number of times it is shown.
Example: Suppose you have 10 clicks and 100 impressions on your LinkedIn post, then your CTR will be 10%.
Client
Client is defined as an individual or organizational entity that purchases the product or service your company offers. He/she is also known as a customer.
Example: Suppose you have purchased an annual growth plan of Mr. E from EasyLeadz, then you become EasyLeadz’s customer or client.
Close
Close means when a sales representative guides the client in such a way that he/she becomes ready to purchase the product or service.
Example: Imagine a sales rep from EasyLeadz guides you to purchase a plan that is the best fit for your business and you make a purchase decision. So, in this way, the sales rep closes this sale.
Close a Deal
Close a deal means closing a purchase agreement in which a potential customer agrees to purchase your product or service. It also resembles that you have made a sale.
Example: Let’s imagine you have recently bought a house from a real estate agent. Here, the agent closes a deal by selling that house to you.
Closed Opportunities
Closed opportunities is a common term involving closed-won and closed-lost opportunities.
Example: If a sales rep closes a successful sale or a deal in which payment from the customer is still pending, it would be considered a closed opportunity.
Closed Question
The closed question is a question asked by the marketers to get a yes or no response while selling a product.
Example: When a marketer asks you “Did you find the Mr. E free trial worthy?”, then the question he asked you is the closed question as that will lead towards closing a deal.
Closed-Won
Closed-won means when the sales rep closes a deal in which the buyer purchases the product or service successfully.
Example: Suppose a client purchases your product or service just after one demo, then this deal would be a closed-won opportunity for you.
Closed-Lost
Closed-lost means when the sales rep tries every possible way to close a deal but the client rejects to purchase the product or service at a very last moment even after going through all the stages of the sales funnel.
Example: Imagine a sales rep approaches a prospect and then further gives him/her a demo. Now the client is ready to buy the product but delaying the payment. After a few days, he has stopped responding to the calls or emails of the sales rep and has not made a payment for the last two weeks. So, this is a closed-lost for the sales rep.
Closing Ratio
Closing ratio is defined as the percentage of the potential customers that a sales rep successfully converts into paying customers in a certain time period. It is usually used to examine the performance of new sales representatives.
Example: Let’s say you send 20 proposals this month, and among those, 5 converted, then your closing ratio is 25%.
Cold Calling
Cold calling is defined as the process of making phone calls to cold prospects to make them interested in a certain product or service.
Example: SDRs making calls to targeted audiences to create awareness about a service or product that might add value to their business.
Cold Emailing
Cold emailing is the process of sending emails to cold prospects to make them interested in a certain product or service.
Example: SDRs send mails to the targeted audience to create awareness about a service or product that might add value to their business.
Cold Outreach
Cold outreach is a process in which the companies engage with prospects either via cold calling or cold emailing, without any prior interaction with them.
Example: SDRs perform both cold calling and cold emailing (cold outreach) to reach their prospects.
Collaborative CRM
A collaborative CRM is a CRM system that lets units both, inside and outside of the company collaborate to improve the customer experience.
Example: Microsoft Dynamics 365, SAP Business One, SugarCRM, Sage CRM, and Pipeliner CRM are some examples of collaborative CRM systems.
Commission
Commission is defined as the payment a sales professional earns when they successfully close a deal. It is usually a percentage of sales revenue.
Example: If a salesperson made Rs.10,00,000 sale and they get a 0.5% commission, they would earn an additional Rs.5,000 apart from their salary.
Compensation
Compensation is defined as the total amount of money or benefits that an employee receives after getting a basic salary, commissions, bonuses, paid leaves, and other allowances.
Example: Imagine your company is rewarding you with an international vacation, then that would be a compensation for you.
100. Complex Sale:-
Complex Sale is defined as a B2B buying process that includes various people and also takes a lot of time to finish the sale cycle.
Example: Sales in the real estate sector are usually complex sales.
Compounded Annual Growth Rate (CAGR)
CAGR is defined as the rate at which the growth of a company is calculated for a specific time period. It is the growth rate that is calculated from the starting investment value to the ending investment value.
Example: Suppose the starting value of your investment is Rs. 15,000, and the final value is Rs. 25,000 in three years, then the CAGR would be 18.56%.
Consumer
Consumer is defined as the person who buys the product or service you provide.
Example: If someone purchases a Netflix subscription then he/she becomes a consumer of Netflix.
Contact
Contact is defined as the stage at which the sales professional and the prospect interact for the first time.
Example: Sales representative contacting a prospect (qualified lead) via email or call.
Content:-
Content is defined as the piece of information on a web page, email, or ad. The content is used to deliver your message via images, copy, video, or other textual or visual ways.
Example: Whatever you post on your social media platforms or websites in the form of texts, images, or videos is content.
Content Management System (CMS)
Content management system (CMS) is a system in which you can create, edit, manage and store your content.
Example: WordPress, Wix, Joomla, and Magento are some examples of CMS.
Conversion
Conversion is defined as the process in which a potential customer converts into a paying client.
Example: When a Mr. E user subscribes to a paid plan.
Conversion Path
Conversion path consists of various steps that a sales rep takes to convert a prospect into a paying client.
Example: This is what the conversion path looks like: (1). Sales representative approaching the user who signed up for a free trial. (2). Booking a demo to explain features, USP (Unique Selling Proposition), and pricing plans. (3). Offering deals and negotiation followed by sending payment link. (4). Receives payment,i.e converted.
Conversion Rate
Conversion rate is defined as the percentage of the prospects that successfully went through the conversion path and became paying clients.
Example: Suppose a website gets 200 visitors in a month and has 20 sales, so the conversion rate would be 10%.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Cost of goods sold (COGS) means the amount of money that is spent on making or producing a good (product or service).
Example: The cost of materials and labor are examples of COGS.
Cost Per Click (CPC)
Cost per click (CPC) is defined as a fee that an online advertiser needs to pay for each click on their ads.
Example: Let’s say if an advertiser paid $100 for an Ad campaign that received 40 clicks, then the CPC would be $2.5 (100/40 = 2.5).
Cost Per Impression (CPI)
Cost per impression (CPI) is defined as the cost an advertiser will pay per 1,000 ad impressions (views of a particular ad).
Example: Imagine, if you paid $100 for a social media Ad campaign that results in 2,000 views, then your cost per impression is $0.05 (100/2000 = 0.05).
Covenant
Covenant is defined as a commitment (formal written declaration) in a bond or contract.
Example: An example of a covenant is a Non-Disclosure Agreement.
Critical Questions
Critical questions are questions that indicate the probability that a potential customer will become a paying customer or if they have doubts about it.
Example: Few examples of critical questions are “How would you solve this problem?” and “Do you like or dislike the product?”.
Cross-Selling
Cross-selling in B2B is defined as the process in which a customer buys a product and they are offered another product as a reward or at a discount.
Example: Whenever Apple sells you an iPhone, then it also sells you Apple iPhone cover complimentary or at a discounted price.
Current Customer
Current customer is an individual or organizational entity who has made a purchase from your company within a specific time period (usually within 12 months).
Example: Let’s say that you want to dine out in your favorite restaurant. Now, when you are currently ordering or buying something from this restaurant, then you become a current customer of the restaurant.
Current Customer Referrals
Current customer referrals are the references provided by the current customers if they know other people who might require the same product or service that the sales representative sold them.
Example: Suppose you bought a grocery item from departmental store A at a 50% discount. Now, you will tell about the discount to your friends and then they also visit the same store to buy that item. In this way, you provide some referrals (current customer referrals) to that departmental store A.
Current Customer Upselling
Current customer upselling is defined as the process in which the sales professionals call existing customers and convince them to spend more by purchasing an upgraded or premium version of what’s being bought.
Example: Suppose, if someone purchases the monthly startup plan of Mr. E and consumes the credits within a week then the sales representative of EasyLeadz would reach out to them to recommend a plan with more credits so that their monthly requirement is fulfilled. If the customer agrees, it is termed as current customer upselling.
Customer
Customer is a person or a company that purchases a product or service.
Example: When you buy something from your nearby grocery store for the first time, you become its customer.
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Customer acquisition cost (CAC) is defined as the total Sales and Marketing cost including advertising costs, the salaries of your sales team and marketing team, etc, to acquire a new paying customer for a product or service. It is calculated by dividing overhead, sales, and marketing costs by the number of acquired new clients in a given time period.
Example: Suppose, if you spend Rs.5,00,000 on Sales and Marketing for a particular month and acquire 50 clients in the same month, then your CAC would be Rs.10,000.
Customer Churn
Customer churn is defined as the percentage of clients who stopped using your company’s product or service for a specific time period. Usually, it describes the loss of clients over a time period to evaluate the business growth.
Example: Imagine, if you start your month with 400 customers and end with 320, then your churn rate is 20% because you lost 20% of your customers.
Customer Experience (CX)
Customer experience (CX) is defined as the impression your company leaves on your customers. It includes every interaction and perception of your customer with the company during all stages of the buyer’s journey.
Example: The best example of great customer experience is Microsoft: customer-centric innovation and engagement.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
Customer lifetime value (CLV) is a metric that helps companies to predict the revenue which they will earn in the future with a single customer account.
Example: Imagine a local restaurant chain with three locations has an average sale of Rs.1000. The regular customer is a local worker who visits two times per week, 50 weeks per year, and over an average of four years. So, the CLV would be Rs.4,00,000.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Customer relationship management (CRM) is software used by companies to monitor, record, manage and track the data of their customers with the goal of increasing customer engagement and revenue.
Example: HubSpot, Microsoft Dynamics, Zoho, Salesflare, and Pipedrive are some examples of CRM software.
Customer Success
Customer success is a proactive mindset and strategy adopted by B2B companies to drive profits, reduce churn rate, retain customers and optimize business with them.
Example: The real-life customer success strategy examples of reputed brands are HubSpot, Facebook, Hyatt Hotels, HelpCrunch, and Zapier
Cycle of Sales
Cycle of sales is the modern sales process that consists of seven stages, such as prospecting for leads, preparation, approaching, presenting, beating objections, closing, and following up.
Example: Firstly, a sales representative will look for the prospects, and then prepare the pitch to approach the prospect. After this, the sales rep will present his product and also handle objections to close the deal. After closing the deal, he will take follow-ups for the feedback, reviews, or generating referrals.
-D-
Dark
Dark is a state in which the prospect has stopped responding to your calls, invites, emails, or interacting with other engagement attempts.
Example: Every sales rep usually has one or more clients, who go dark on them.
Data
Data is a set of qualitative or numerical information collected and analyzed by the companies to plan, forecast, predict or compute.
Example: Record of customers is a kind of data stored by company A to perform business analysis.
Data Entry/Processing
Data entry/processing is a process in which the information is manually recorded to retrieve and use later. These days, most of this data is stored in CRM systems.
Example: Updating your customer’s information in your company’s CRM is an act of data entry/processing.
Data-Mining
Data-mining is a process of extracting new information about potential leads from large databases.
Example: The real-life examples of Data mining are E-commerce, the Retail sector, AI, Research, Mobile service providers, etc.
Day Sales Outstanding (DSO)
Day sales outstanding (DSO) is the time that it takes for a company to collect its payment for a sale on a monthly, quarterly, or annual basis.
Example: Imagine that during the month of March, company A made a total of Rs.400,000 in credit sales and had Rs.380,000 in accounts receivable. There are 31 days in March, so company A’s DSO for March would be 29.45 days.
Days to Term Sheet
Days to term sheet is the time that it takes from first contacting the client to the time the deal is closed.
Example: Suppose, a sales rep at EasyLeadz discovers a quality lead on Monday; reaches out to it via call or mail on Tuesday, and on Wednesday they both have a demo of Mr. E tool. Finally, on Thursday, the prospect becomes ready to purchase the product and on Friday, he makes a payment. So, these 5 days will be included in the terms sheet as the days taken to close a deal.
Deal Closing
Deal closing or closing a deal is the process of making a sale wherein the potential customer is ready to buy a product or service.
Example: Suppose one of your prospects is ready to buy your company’s product under your guidance. So, in this way, you close a deal.
Deal-Flow
Deal-flow is a metric indicating the average rate at which salespeople have leads in a pipeline.
Example: Usually startup investors use deal flow to predict the estimated growth of the startup.
Decision-Maker
A decision-maker is a person in an organization who has the authority to make the final purchase decision.
Example: Usually C-level executives like the CEO, CTO, COO, or CXO are the decision-makers of a company.
De-Dupe (Deduplication)
De-Dupe or deduplication is the process of removing duplicate data using filters or other ways.
Example: Removal of multiple entries of the same customer that are stored in a database at multiple locations.
Deferred Revenue
Deferred revenue is the payment received in advance by the company for products or services that are going to be delivered in the future.
Example: Common examples of deferred revenue are rent payments received in advance, and prepayments received for annual subscriptions.
Deliverables
Deliverables are the quantifiable products or services that need to be delivered to the customer.
Example: Proposals, Progress Reports, and Customized Samples are some examples of deliverables.
Demand Generation
Demand generation is a marketing strategy for creating buzz, excitement, interest, or awareness about a company’s products and services among the public.
Example: Email marketing, content marketing, social media marketing, or SEO are the demand generation activities.
Demo
Demo is a detailed presentation or demonstration, usually given by the sales representatives on the products or services they are selling.
Example: When you visit the homepage of EasyLeadz, you will find a CTA “Watch Demo”. As you click on it, you will automatically be forwarded to the demo video of the tool Mr. E by EasyLeadz.
Demo Goals
Demo goals are the goals that a sales professional sets for the number of demo presentations he/she will give in a specific time period.
Example: Let’s say a sales rep from company A has set a goal of giving 200 demos in a month. So, 200 demos are the demo goals for that sales rep.
Demo-to-Close Conversion Rate
Demo-to-close conversion rate is defined as the number of closed deals in a given time period divided by the total number of demos that made those wins.
Example: Let’s say a sales rep schedules 50 demos and among them, only 20 are converted into sales. So, the demo-to-close conversion rate will be 40%.
DevOps
DevOps is a compound of “development” and “operations”. In simple words, it is an automated process that takes place based on how a client reacts.
Example: Suppose, if a customer clicks on an email that is part of a marketing campaign and engages with it, then another link is sent to them on behalf of their click.
Dialer
Dialer is a device or software that automates the process of making phone calls for sales professionals.
Example: HubSpot Call Tracker, Aircall, CloudTalk, and RingCentral are some examples of dialer software.
Direct Mail
Direct mail is a kind of marketing where promotional materials (written or electronic) are sent directly to a customer’s home address through a post office.
Example: Postcards with an offer, coupons, free samples, brochures, catalogs, etc.
Direct Response Marketing
Direct response marketing is a marketing strategy that directly targets potential customers to create interest in a product or service.
Example: Social Media Ads, Referral Programs, Upselling, Giveaways, and Contests are some examples of direct response marketing.
Direct Sales
Direct sales refer to the method of selling a product or service to the customer face-to-face in a location other than the retail stores.
Example: A common example of direct sales is the selling of Herbal Life nutrition products. The salespeople who are selling these products usually visit customers’ homes to make a sale.
Discount
Discount is a reduction in the price of a product or service, usually done for promotional or marketing purposes, in order to increase sales.
Example: Flipkart offers great discounts on electronics during the Diwali festival.
Discovery
Discovery is the first stage at which the sales rep makes any kind of contact with a prospect such as just going through his/her profile on LinkedIn for the first time.
Example: You finding some valuable prospects on LinkedIn just by viewing their profiles is no less than a discovery.
Discovery Call
A discovery call is the first phone call that a sales representative makes to a potential client with the aim of qualifying them for the next step.
Example: A sales rep calling a prospect for the first time after finding his LinkedIn profile valuable.
Display Name
Display name or From name is an email address that will make recipients open and read the message only if they find the name familiar.
Example: When you send an email, your email address is a display name for your recipient.
DOA
DOA is an acronym for dead-on-arrival. A sales pitch, customer, product, or service can be DOA which means on receiving or arrival, the product or service is not up to the mark.
Example: Suppose even after using a good sales pitch, the customer does not purchase the product for any reason. Then, that sales pitch is dead on arrival (DOA).
Doing Business As (DBA)
Doing Business As (DBA) means rebranding. The term is generally used to inform the client that the business is now operating under a different brand name than the original one. Usually, a company is said to be a “DBA” when the name under which they operate its business differs from its registered name.
Example: A perfect example of DBA is EasyLeadz, which has its registered name as “SponsifyMe” but operates as “EasyLeadz”.
Double Trigger
Double trigger is a scenario in which two events or triggers happen during an acquisition that accelerates the process of vesting benefits if an employee leaves the organization or is fired without due cause.
Example: Some examples of double-trigger accelerations are the sale of the company and the transfer in ownership of the startup.
Drag-Along Rights
The drag-along rights clause in an agreement provides the authority to the majority of shareholders of a firm by which they can “drag along” the minority of shareholders to sell their stakes in the company during the acquisition.
Example: Company X is listed on the exchange. A larger company, Y, has managed to buy more than 51% of X’s shares from the markets and other owners of the company, due to which there is an acquisition noted in the future for X by Y. However, Y wishes to own company X “fully”, which means they wish to hold a 100% stake in X without sharing any ownership with minority shareholders. So in this scenario, the majority of shareholders would force the minority shareholders to sell their stakes. In other words, the majority of investors are putting up their drag-along rights.
Draw
Draw is the amount of money that sales representative receives in advance in order to ensure they are properly compensated when they are starting their job. It is then repaid through the commissions the sales rep earns.
Example: Suppose, company A gives a draw of Rs. 500 to every sales rep.
Draw on Sales Commission
Draw on sales commission is defined as an advance payment in the form of compensation that sales professionals receive against expected commissions or earnings. It is also known as “Draw Against Commission” or simply “Draw”.
Example: Suppose, if your projected commission is Rs. 4,000 a month, the company could offer a draw of Rs.2,000 a month. That means you would be paid Rs.500 a week. At the end of the month, if you fulfilled the Rs. 4,000 sales goal, you would be paid an additional Rs. 2,000.
Drip Campaign
A drip campaign is an email marketing campaign that sends an automated response after a certain time period.
Example: Suppose if someone subscribes to your newsletter, you can set a drip campaign prior that would send a welcome email and after few days would send the great offers on your product.
Drive-By Selling
Drive-By selling is a way to sell in which the sales representative stops the leads or potential customers in malls or markets to speak with them about the product or service.
Example: To illustrate the concept of drive-by selling, let’s take an example of vendors who sell balloons or pens on busy roads. They are drive-by sellers as they stop their customers in between the roads to sell their products.
-E-
EBITDA
EBITDA stands for Earnings Before Interest Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization.
Example: EBITDA is a term used by large companies for accounting standards.
E-Commerce
E-commerce is a business model that allows individuals and companies to buy and sell goods and services over the internet (electronic network).
Example: Amazon, Flipkart, and Shopify are some examples of e-commerce platforms.
Email Automation
Email automation is the process of automating prewritten emails by scheduling them in advance to target the right recipients.
Example: Some examples of email automation include: welcome emails, onboarding emails, transactional emails, re-engagement emails, or survey/feedback emails.
Email Marketing
Email marketing is a marketing strategy that uses emails in order to target potential customers or generate new leads. It can also be used for nurturing your prospects and converting them into paying clients.
Example: Some tools for email marketing are HubSpot Email Marketing, Sender, Sendinblue, Omnisend, SendPulse, Benchmark Email, Mailchimp, MailerLite, etc.
Email Tracking
Email tracking is a way to monitor or track the performance of an email marketing campaign. It provides analytics to marketers to see how many of their emails have been opened, clicked on, and responded to.
Example: Some tools for email tracking are snov.io, MailTrack, or Orangebox.
Emotional Sale
Emotional sale is a technique of inducing either positive or negative emotions in the buyer to create a desire to purchase the product or service being offered.
Example: Coca-Cola, the most famous beverage company in the world, used an emotional marketing strategy by replacing its logo with customized messages (written by its users) on the cans through online customization. These messages were like “I promise to smile more just for you”, or “I’m not the best at compliments but I’ll try”.
Employee Engagement
Employee engagement is defined as the strong commitment and connection of the employee towards the company and vice-versa.
Example: An employee striving to improve the company’s well-being and profitability by putting his/her personal motives behind it.
Engagement
Engagement is a process of keeping the audience (customers, employees, management, etc.) interested in a company and invested in it due to its benefits to the audience.
Example: Some examples to keep your customers engaged are sending them welcome messages, creating personalized content, and designing an exclusive loyalty program for them.
Enrichment
Enrichment is a process of upgrading or improving the product or service with valuable features to deliver a better customer experience.
Example: Mr. E by EasyLeadz is a contact data provider tool that provides phone numbers of the top management along with their email ids as complimentary. So, providing email ids is a way to enrich the tool for a better customer experience.
Enterprise
An enterprise (in the context of sales) is a relatively large organization that consists of multiple departments or levels with thousands of employees, and also requires multi-layer software systems for collaboration.
Example: Microsoft, IBM, Apple, and Amazon are some examples of enterprise companies.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
ERP is software used by enterprises or companies to centralize inventory, shipping and fulfillment, purchasing, product planning, HR, and many other functions.
Example: Netsuite, SYSPRO, and Epicor are some ERP products.
Entrepreneur in Residence (EIR)
Entrepreneur in residence or executive in residence (EIR) refers to the position most often held by successful entrepreneurs in private equity firms, venture capital firms, startup accelerators, or law firms.
EOD
EOD is an acronym for “End of Day”. It is also considered the end of the business day (usually at 6 pm).
EOM
EOM is an abbreviation that stands for “End of Month”.
EOQ
EOQ is an abbreviation that stands for “End of Quarter”.
EOY
EOY is an abbreviation that stands for “End of Year”.
Equity
Equity is defined as the value of ownership in any business or privately held company. To buy shares of a company means to buy a small part of that company which is equity.
Example: Suppose, company X had two lakh outstanding shares, and if the company’s current market value is Rs.100 per share. Then the company’s market value of equity would be 200 lakhs.
-F-
FAB
FAB is an acronym for features, advantages, and benefits, which are used by sales professionals and marketers to highlight the product or service value in front of their customers. It ultimately helps sales representatives to create their unique selling point.
Example: The FAB model for Mr. E by EasyLeadz, the contact data provider tool would be:Features: The key feature of Mr. E tool is to provide 100% accuracy.Advantages:- The advantage of this tool is that if you find any phone number wrong, then your credit for that will be refunded. Benefit:- The core benefit of getting your credits refunded is your credits will not be wasted.
Fair Market Value (FMV)
Fair market value (FMV) is the current price at which a business, property, or asset would sell in an open and competitive market.
Example: Imagine, if you are selling a used car, then the highest bid received from a buyer is the fair market value (FMV).
Feature
Feature refers to the function of a product that can solve a potential customer’s problem.
Example: The feature of Mr. E by EasyLeadz, the contact data provider tool is to provide 100% accuracy which means if you find any phone number wrong, your credit for that will be refunded.
Field Day
Field day means a day when a candidate has to work with experienced working professionals assigned to the position he/she is being interviewed for.
Example: A civil engineering graduate joins the organization, so his first day at his organization would be a field day for him.
Field Sales Rep
Field sales rep is a traveling salesperson who reaches out to the prospects and pitches products/services by visiting them.
Example: Pre-covid, sales rep used to visit prospects to pitch and sell them their products or services.
Firmographics
Firmographics are defined as the criteria that is used to identify a target audience or target market for B2B marketing. It consists of a set of descriptive attributes of prospective organizational customers that can be used by B2B companies to classify their firms into relevant market segments.
Example: Some examples of firmographics are location, revenue, industry, budget, market share, business volume, organization type, employees, etc.
Fiscal Year
Fiscal year is a year of the financial accounting period that is used by the governments and companies for accounting, budget planning, financial reporting, strategy formulation, taxation, performance assessment, and other purposes.
Example: In India, the new fiscal year begins on 1st April and ends on 31st March next year.
Flywheel
The flywheel is a new method to conceptualize the sales process where customers are thought of as an output. It replaces the sales funnel and shows that awareness, engagement, and delight can happen at any stage of the sales process. Basically, it helps you close more deals with less effort.
Example: Amazon uses the concept of Flywheel in all their businesses. Even, Amazon Web Services (AWS) has also used this concept to speed up its business growth.
Forecasting
Forecasting is the process of predicting the sales performance for a specific or forecast period using past data, which is further used for task planning and the setting of standards. In this, companies use the forecasting technique to estimate their likely future revenues during a forecast period.
Example: Suppose Company A is forecasting its revenue for the upcoming months.
Footprint
Footprint refers to the steps that any normal order should go through from acquisition to delivery.
Example: Imagine, yourself ordering a laptop on Amazon, as you place your order, you will get every minute detail such as when was the order picked, when it will be shipped, or when it will be delivered. All these details are referred to as footprints.
Fortune 500
Fortune 500 is an annual listing of the 500 most successful companies in the US based on their revenue and published by Fortune magazine.
Example: Click here to get the list of Fortune 500 for the year 2021.
Forward Revenue
Forward Revenue is defined as the recurring revenue estimated for the next 12 months.
Example: Public SAAS and COOS are based on this specific data. The current median point for forward revenue is 5.0 X.
FUD
FUD is a sales and marketing acronym that stands for Fear, Uncertainty, and Doubt. In marketing, fud can be a trick to make your customers doubt other brands.
Example: People talking negatively about NFTs, Cryptocurrency, or Bitcoin creates FUD among the investors.
-G-
Gated Content
Gated content is premium content that is accessible only by filling out a web form and providing personal information like email addresses.
Example: Industry reports, White papers, or e-books are usually considered as gated content.
Gatekeeper
Gatekeeper refers to an employee who controls access to a decision-maker.
Example: Receptionist, Secretary, or Personal Assistant.
General Manager
General manager is an executive who generally leads a branch of a company by looking at its daily operations, performance, and profitability.
Example: The decision-makers holding the titles of CEO or President are usually the general managers of their respective businesses.
Global Business Unit (GBU)
Global Business Unit is a semi-autonomous unit of a multi-national company that focuses on a particular industry or a specific set of products, services, and functions, operating on a global scale.
Example: Some global business units are KFC, Starbucks, and McDonald.
Goodbye Message
Goodbye message is an automated message that is sent to the users from your list who have unsubscribed. These kinds of messages contain a re-subscribe option if the user mistakenly unsubscribes.
Example: You often receive a mail like “It’s sad to see you go”, whenever you unsubscribe from the newsletter subscription of any company.
Go-To-Market (GTM) Strategy
Go-To-Market (GTM) strategy is a plan or a roadmap consisting of a set of actions that a company takes to optimize sales and marketing resources for promoting a new product or service.
Example: FitBit, an American manufacturer of activity trackers used the GTM strategy while launching Smart Coach, a training app.
Goal-D Card Incentive Program
Goal-D Card Incentive Program is a sales incentive program to encourage the sales teams for positive results.
Example: Goal card is an electronic card that tracks demos, calls, or sales reports which helps in making comparisons and driving positive results.
GPCTBA/C&I
GPCTBA/C&I is an acronym for Goals, Plans, Challenges, Budget, Authority, Consequences, and Implications. It applies to anything and everything about modern sales and marketing.
Example: GPCTBA/C&I applies to anything and everything about modern sales and marketing.
Gross Margin
Gross margin is defined as the total sales minus the cost of goods sold (COGS).
Example: Suppose, your company’s total sales for the year are Rs.1,00,000 and your COGS is Rs.40,000. Then your company’s gross margin is Rs.60,000.
-H-
Historic CLV
Historic CLV is defined as the sum of all profits from different customers’ past purchases within the store.
Example: Historic CLV comprises information based on existing customer data and a given time period.
Horizontal
Horizontal is a particular offering or a sole market opportunity for a company.
Example: Purchasing all the other medical CRMs so that you can become the only medical CRM provider.
-I-
Ideal Customer Profile (ICP)
Ideal customer profile is a kind of customer that has all the positive characteristics that you might want in a client: their age, gender, physical appearance, location, social status, income, or other related factors which increase the chances of making a purchase.
Example: For the Aldo company, the Ideal Customer Profile would be a woman who can afford expensive, imported handbags.
Inbound
Inbound refers to letting the potential prospects come to you due to the interest-driven in them by sales or marketing techniques.
Example: Person reaching out to you on LinkedIn to enquire about your services.
Inbound Lead Velocity (ILV)
Inbound lead velocity is defined as the rate at which the percentage of your qualified leads increases on monthly basis. It measures pipeline development. It can be calculated by first subtracting the number of qualified leads last month from the number of qualified leads this month. Then divide the result by the number of qualified leads last month and multiply by 100 to convert it to a percentage.
Example: Suppose, you have 70 qualified leads this month and you had 40 qualified leads last month. Now, subtract 40 from 70. Then, divide 30 (70-40) by 40 and multiply the result by 100. So, here the ILV is 75%.
Inbound Marketing
Inbound marketing is a strategy to build meaningful relationships with prospects to fulfill their interests, or needs and address their pain points.
Example: Blogging, Content marketing, Email marketing, or SEO.
Inbound Sales
Inbound sale is a process of getting sales by focusing on customers’ needs wherein deals close as a result of customers’ direct approach.
Example: Viral vlog, ebooks, or selling through social media.
Independent Software Vendor (ISV)
Independent software vendor (ISV) is an organization that makes and sells software, designed for particular markets.
Example: Microsoft, Oracle, Apple, Google, IBM, or Hewlett-Packard.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) is a type of cloud computing that provides online computerized assets such as networking, virtualization, and pay-as-you-go storage. It’s one of the three main types of cloud services (SaaS and PaaS).
Example: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Docker, Zapier, etc.
Initial Public Offering (IPO)
IPO is the selling of stock issued by a private company and offered to the public for the very first time in order to raise more capital.
Example: IPO of LIC in 2022.
InMail Messages
InMail messages refer to a premium LinkedIn feature that allows you to send a message to another LinkedIn member, whom you are currently not connected with.
Example: Suppose you want to send a message to the CEO of an SME, but are not connected to him/her. So, if you have a LinkedIn premium membership then you will be able to message without having a connection.
Inside Sales Rep
Inside sales representative is a salesperson who directs the sales processes remotely over the phone or online.
Example: During the times of Covid, every sales rep was an inside sales representative.
Intellectual Sale
Intellectual sale is unlike an emotional sale, which tries to address prospects’ requirements and guide them to realize why a product or service is a quick solution to their problem.
Example: Mr. E by EasyLeadz, the B2B contact finder tool, helps in bridging the gap between you and your prospects by providing you their phone numbers directly. This pitch contributes to intellectual sales.
IVR Systems
IVR systems are interactive voice recording systems.
Example: When you call a company and then you hear “press 1 for language, press 2 for customer support, press 3 to speak to the operator”, that is based on the IVR system.
-K-
Key Accounts
Key accounts are elite clients prioritized by a sales representative for customer success; churn from these customers would be a loss to the company’s revenue.
Example: VIP customers who make repeat purchases.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are the most relevant measurable metrics that evaluate the progress of a company or an individual towards achieving the desired goals and objectives.
Example: KPIs help in accessing the progress made by an individual from the beginning.
Kickers
Kickers are financial rewards or monetary bonuses offered to encourage sales professionals to close more deals or exceed quota.
Example: Let’s say your boss offers you an additional Rs.10,000 to close 5 more deals.
-L-
LAIR
LAIR is an acronym that stands for Listen, Acknowledge, Identify the Objection, Reverse the Objection. It is a method for handling sales objections.
Example: LAIR uses active listening and reframes your prospect’s objection in a way that represents why taking your offer will be beneficial for them.
Land and Expand
Land and expand is a sales strategy for landing that means onboarding a new client and expanding him/her through upselling. In simple words, it means getting the customers to buy more or extending the scope of your product or service.
Example: After three months of onboarding a new client, most sales rep tries to expand that client through upselling.
Landing Page
A landing page is a web page created for the purpose of lead generation using a marketing campaign. It contains a specific offer and encourages prospects to take action. They end up on a landing page after they have clicked on an ad or a marketing email.
Example: You can take an example of Get Response, which is an interactive landing page.
Lead
Lead refers to a prospect or a potential customer. It can be an individual or a company expressing interest in your product or service in some way.
Example: Suppose you have posted about a discount offer for a particular product or service on your LinkedIn and now you are getting queries about it. So, those queries are your leads.
Lead Generation
Lead Generation is a process of generating leads and nurturing them into paying customers through blogging, podcasts, ads, or outbound marketing.
Example: Some ways to generate leads are cold emailing, cold calling, referrals, online content, or ads.
Lead Nurturing
Lead nurturing is a process of building long-term relationships with potential customers using various marketing techniques that develop their interest in your product or service.
Example: Email drip campaigns, direct mails, email newsletters, sales calls, personalized emails, or blog posts are some examples of lead nurturing.
Lead Qualification
Lead qualification is the process of assessing whether a prospect has the attributes of your company’s ideal client such as the likelihood of buying your product, sufficient purchasing ability, or purchasing intent.
Example: Few examples of lead qualification are rule-based lead qualification, internal marketing qualification, internal sales group qualification, or external third-party qualification.
Lead Scoring
Lead scoring is a method for evaluating and ranking leads based on different criteria.
Example: In this, a number scale is used, and a relative value is assigned to each lead so that the sales rep can focus on the leads that can be closed soon.
Lifetime Value (LTV)
Lifetime value (LTV) is a predicted value for revenue that a customer will generate before they churn.
Example: Suppose a customer pays you Rs.1,00,000 per year where your gross margin on the revenue is 70%, and that client type is predicted to cancel at 16% per year, then the client’s LTV is Rs.4,37,500.
LinkedIn
LinkedIn is a social networking platform specifically for the business community.
Example: LinkedIn
List Hygiene
List hygiene is the process of cleaning a database and updating it regularly to keep your list relevant and fresh by deleting inactive, outdated, and incorrect entries.
Example: Mr. E by EasyLeadz works in real-time and hence the data is updated, relatively fresh, and accurate.
Loss Aversion
Loss aversion is a psychological effect due to which people feel the pain of losing more severe than the pleasure of gaining.
Example: Suppose, you lose a regular client to a competitor and suppose you win a client from the competitor, you will instead of celebrating the latter situation, will sink and mourn over the former situation.
Loss Leader
Loss leader is a strategy for pricing where the prices of a product are lower than its market cost to boost the sales of more profitable or highly-priced products.
Example: In supermarkets, combo offers on daily essential products are typical examples of loss leaders.
Low-Hanging Fruit
Low-hanging fruit refers to the goals that are easy to achieve or the prospects that can be converted easily.
Example: A woman visiting a bag store with an intention of buying is the low-hanging fruit for the salesperson in the store.
LTV:CAC
LTV:CAC is a ratio of lifetime value to customer acquisition cost that measures the costs to acquire a customer and a business’ lifetime value relationship with that customer.
Example: Suppose, if your customer lifetime value is Rs.7,000 and your expenses to acquire a customer are Rs.4,000, then your LTV:CAC ratio would be 7:4.
-M-
Machine Learning (ML)
Machine learning is a branch of artificial intelligence (AI) and computer science that enables software applications to be more accurate in predicting outputs without being programmed to do so.
Example: Deep Learning, Virtual Assistant, Speech Recognition, Analytics, Pattern Recognition, and Medical Diagnosis are some real-world examples of ML.
Margin
Margin is the difference between the selling price of a product or service and the cost of production.
Example: Suppose the selling price of product X is Rs.2000 and its cost of production is Rs.1500. So, the margin for product X would be Rs. 500 (2000-1500).
Mark-up
Mark-up is defined as the amount added to the original cost price of a product or service to cover overhead and profits.
Example: Let’s say you buy a laptop for Rs.40,000, you must sell it for more than Rs.40,000 to make a profit.
Marketing
Marketing is a plan, set of actions, and strategies that a company uses for the promotion of products or services, with the ultimate goal of selling them.
Example: Branding, Advertising, Direct Marketing, Social Media Marketing, Content Marketing, In-Store Marketing, and Flat Pricing are some examples of marketing.
Marketing Automation Platform
Marketing automation platform is a technology that automates the manual processes in sales and marketing so that companies can generate, nurture, and convert leads more effectively.
Example: HubSpot, ActiveCampaign, Marketo, Mailchimp, and Sendinblue are some examples of marketing automation platforms.
Marketing Qualified Lead (MQL)
A marketing qualified lead is a lead that has been qualified as being sales-ready based on lead scoring criteria.
Example: MQL is the high intent prospect who has shown the most interest in a company’s product or service due to the marketing efforts.
Master Services Agreement (MSA)
Master services agreement (MSA) is the agreement between two companies where one agrees to manage particular marketing activities for the other party. These activities consist of building the other company’s online presence, creating an advertising campaign, or formulating a market plan.
Example: An agreement between a digital marketing agency and an e-commerce company.
Messaging
Messaging is the means of communicating your brand’s value proposition, and the benefits you offer to your target audience.
Example: ‘Just do it’ from the famous brand Nike is an example of brand messaging.
Metrics
Metrics are quantities that are used to track performance, determine cost efficiency, make accurate revenue forecasts, and assess profitability for a company.
Example: Sales, customer satisfaction, net promoter score, gross margin, churn rate, profit margin, etc.
Mid-market
Mid-market refers to a business occupying the middle range of the market, between small and large businesses, based on their revenue and employee size.
Example: Chalet Hotels Ltd., Modicare Ltd., and Colorbar Cosmetics are some examples of mid-market companies.
Middle of the Funnel (MOFU)
Middle of the funnel refers to the middle stage of the buyer’s journey where the quality leads already exist in your database and are interacting with your brand.
Example: A prospect booking a demo of Mr. E tool with the sales professional of EasyLeadz.
Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
Minimum viable product is the first form of a product or service which is built with enough basic features; just to satisfy early users who will give their feedback, and verify product-market fit & demand for further development.
Example: Airbnb, Dropbox, Amazon, and Facebook are some examples of minimum viable products.
Mirroring
Mirroring is a powerful sales technique used to build a strong connection with prospects through adopting their specific behavioral characteristics.
Example: Suppose if clients cross their legs while sitting down, the sales professionals will mirror the same position to foster a feeling of trust among them.
Monday Morning Meeting
Monday Morning Meeting is a practice of conducting a sales meeting at the beginning of every week, usually on Monday mornings, to discuss and communicate the important work-related information.
Example: A team meeting that is held on every Monday morning at your workplace to plan the entire week is a Monday morning meeting.
Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)
Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) is defined as an amount of regular and estimated income that a company expects to receive per month, usually for subscription-based businesses. To calculate MRR, divide ARR (Annual Recurring Revenue) by 12.
Example: Imagine if you have 5 customers and they pay you Rs.500 per month, then your MRR would be Rs.2500.
Multi-threading Sales
Multi-threading sales refer to deals in which your sales team is connected with multiple decision-makers from the buyer’s side.
Example: Imagine a sales rep of Company A is connected with all the co-founders of Company B to close a deal.
-N-
Name Based Rapport
Name-based rapport is the effective utilization of “Third Person Selling” to drive interest and guide your potential customer to be open-minded with your ideas.
Example: Suppose Company A recommended the tool, Mr. E by EasyLeadz to Company B and it buys the tool because of the recommendation. Then, here EasyLeadz’s name-based rapport helps it to close a sale.
Name Dropping
Name Dropping is a beneficial sales tactic where you use names of famous brands you had an opportunity to work with to build a good impression on customers.
Example: EasyLeadz can use the name of Microsoft to build a good impression on its target audience.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural language processing (NLP) is the branch of artificial intelligence, and computer science, where computers or machines have the ability to understand the text and spoken words in much the same way human beings can.
Example: Alexa or Siri use NLP to take what you say and execute commands with it.
Needs Assessment
Needs assessment is a process to identify the prospects’ pain points so that you can offer them the right solution.
Example: Suppose a company works to understand who its competitors are to present a more attractive product to their customers. Then Needs Assessment will help the company discover what their product requirements are, how they can improve them, and how to market them effectively to their target audience.
Negotiation
Negotiation is a bargaining process or a strategic discussion between two persons (usually a business owner and a customer) to attain an acceptable mutual agreement.
Example: A vendor, negotiating with a customer over the price of a sale.
Net Asset Value (NAV)
Net asset value refers to the value of a company’s total assets minus the value of its total liabilities per share.
Example: Let’s say company X has assets worth Rs.50 lakhs and has liabilities of Rs.20 lakhs, so company X’s NAV would be Rs.30 lakhs.
Net New Business
Net new business means when a prospect has been newly converted into a paying customer and started generating revenue.
Example: Any signed-up user purchasing a subscription plan for the first time becomes the new business for the company.
Net Promoter Score (NPS)
Net promoter score is a customer-satisfaction rating scale from 1-10, determining how likely a customer is to recommend your company to others.
Example: If a customer rating is 10, then the customer is really happy with your service and is the most likely to recommend it to others. If a customer rating is 1, then the customer is not happy with your service.
New Customer
A new customer is a customer who has never placed an order before.
Example: Any signed-up user purchasing your product for the first time becomes the new customer for your company.
Newsletter
Newsletter refers to the informative emails that are sent either every week or month. This improves brand visibility and awareness.
Example: How to Write Newsletter?
Non-Sales-Related-Activities (NSAs)
Non-sales-related activities are tasks that don’t directly lead to sales.
Example: Administrative tasks, paperwork, voicemail checking, making personal calls, or surfing the web.
-O-
Objection
Objection refers to any questions or concerns that a prospect expresses after your pitch, which can hinder the closing of a deal.
Example: Pricing, Trust, and Timing are some common objections raised by prospects.
Off-Schedule
Off-Schedule refers to a salesperson who is not ready to do the agreed necessary tasks to fulfill his quota.
Example: An employee not meeting his or her sales targets.
On Track Earnings/On Target Earnings (OTE)
On track earnings or on target earnings are common sales pay structures including a base salary and an additional amount of commission.
Example: Suppose a sales rep meets his quotas then he will get an additional commission along with his base salary.
Onboarding
Onboarding refers to the process of introducing a new customer to your product/service. It is also a method of introducing a recently hired employee into your team.
Example: An onboard call is conducted for the new customers to make them familiar with the product/service.
Operational CRM
Operational CRM is the most common CRM system that helps companies to manage their regular sales, marketing, and customer service operations.
Example: Salesforce, Agile CRM, HubSpot CRM, and Zoho are few examples of operational CRM.
Opportunity
Opportunity is a lead that is expected to have a higher chance of making a purchase or subscribing based on a set of criteria. It is also known as SQL (Sales Qualified Lead).
Example: Any potential lead that inquires again and again about your product or service.
Optimization
Optimization is a process of improving a system, service, or product to attain full functionality or efficiency and generate maximum output.
Example: Optimizing a blog by adding more internal links.
Opt-In
Opt-in is a process in which an individual subscribes for a newsletter or gives a company permission to send them emails.
Example: A person subscribing to a company’s newsletter for getting product updates.
Organization Structure
Organization Structure is a system that shows the hierarchy, lines of authority, and interrelationships in an organization.
Example: Inline, Functional, Staff Aligned, or Project-based are some ways to create an organizational structure.
Organization
Organization is a group of people working together and formally bound by a shared identity (a company) with a common purpose (business growth).
Example: Corporations, Political organizations, International organizations, Government organizations, etc.
Outbound Sales
Outbound Sales are the sales in which the seller (a sales rep) directly reaches out to a prospect via cold outreach or social media with the goal of closing a deal.
Example: Cold calls, cold emails, or door-to-door visits.
Overcoming Objections
Overcoming Objections refers to the winning customer’s trust once they have addressed their issues or concerns.
Example: Free Trials, Case Studies, and Testimonials help in overcoming objections and closing deals.
-P-
Package Sale
Package sale is a sale in which multiple products/services are being offered at one presentation.
Example: Sales done in the companies like Amway, Forever, Oriflame, etc.
Pain Point
Pain point is an important point that a sales professional must know while selling to identify the prospect’s needs and offer solutions.
Example: Many B2B companies are not able to reach their prospects timely. So, Mr. E by EasyLeadz, the B2B contact finder tool bridges the gap between the companies and their prospects by providing direct phone numbers.
Past Customer
Past customer refers to a customer who has stopped purchasing a product/service for a year or over.
Example: A customer who no longer pays for service becomes a past customer of a company.
Payment
Payment is defined as an act where the customer mutually agrees with the seller and makes a transaction. This transaction can be monetary or in kind.
Example: Customer subscribing to Mr. E’s paid plan.
Performance Plan
Performance plan is a plan made by an underperforming sales rep to reach performance goals in a given period. It is also known as a Performance Improvement Plan (PIP).
Example: Performance plan helps the sales rep to reach his target efficiently and effectively.
Personalization
Personalization is the process of adjusting the offer, email campaign, or product/service so that it fits the requirements of a particular customer.
Example: A personalized newsletter for a new client.
Pipeline
Pipeline (in the context of sales) is a sales pipeline that consists of expected closures for a given period.
Example: Suppose a sales rep has 4 expected closures for a current week, then it means there are 4 leads in his pipeline that will help him to reach his target.
Pitch
Pitch is the act of marketing your products or services. It refers to communicating about a product or service usually by a sales rep.
Example: Sales pitch, marketing pitch, email pitch, phone pitch, or follow-up pitch.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Platform as a Service (PaaS) refers to the selling of an online platform with tons of integrations and apps.
Example: Salesforce, Zapier, or Slack.
Plays
In terms of sales, a sales play is a repeatable sales offering that is aligned to deliver the highest chance of closing a deal with a specific set of customers during a given time period.
Example: A sales play helps in establishing the best way to pitch the product/service or to make a sale.
Point of Contact (POC)
Point of Contact refers to the person or unit representing an entity usually assigned to ease decision-making and coordinate the flow of information to and from the entity.
Example: Customer Service Department is a POC for an organization.
Positioning Statement
Positioning statements are the statements and questions that many sales professionals use at the start of a sales call to engage a prospect and identify their pain points.
Example: “Mr. E by EasyLeadz bridges the gap between you and your prospects by providing you their phone numbers directly” is a positioning statement.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive Analytics refers to the tool that uses historical data, machine learning, and statistical algorithms to forecast future outcomes with regard to business growth.
Example: Identifying customers that are likely to abandon a product or service.
Predictive CLV
Predictive CLV is a considered accurate method that businesses utilize to assess a customer’s total lifetime value.
Example: Predictive CLV helps to estimate revenue from a certain customer for a specific time period.
Presentation
Presentation means presenting actual sales, also known as demos, aiming to make an emotional and intellectual deal.
Example: Demonstration of any product or service.
Presidents Club
Presidents Club is a prestigious award in a sales organization given to elite performers due to their exemplary achievements.
Example: Generous prizes, vacations, dinner, etc.
Pressure Sales Words
Pressure sales words are any words that cause some stress on your prospects.
Example: “This offer is valid till Monday, 7 pm” is a pressure sales phrase.
Price-Build-Up
Price-Build-Up refers to the act of making a suitable point to discuss the price of the products/services properly.
Example: Negotiation meetings to negotiate the pricing of a specific product.
Pricing/Price
Price refers to the amount of money that the customer needs to pay in order to get a product or service.
Example: MRP of any product.
Primary Influences
Primary Influences refer to the groups of people classified as customers, employers, stockholders, lenders, and vendors.
Example: Important decisions in an organization are made by primary influences like the Board Of Directors.
Pro-Rata
Pro-Rata is defined as the proportional allocation of income, expenses, and other quantities to their components based on the original total amount share of that component.
Example: Suppose a landlord charges a tenant Rs.5000 for staying in a room for 15 days, where the rent is Rs.10000 per month.
Pro-Rata Rights
Pro-Rata Rights refer to the right of first refusal for investors that allow them to buy equivalent equity amounts when dilutions of their initial investments occur.
Example: If an investor owns 10% of a company after their first investment and has the right to purchase any more than 10% of the company in a subsequent round, then they have pro-rata rights.
Procrastination Objection
Procrastination is a term for those who hold the stocks of a company.
Example: Lack of Budget, Trust, Need, or Urgency are some procrastination objections.
Procurement
Procurement is the process that includes demand assessment, bid reviews, approval requests, and transaction logging to find and acquire goods and services.
Example: Contract close-out or identifying potential service providers.
Product
Product refers to anything (item, service, or process) that meets a need and is offered in the market.
Example: Mr. E by EasyLeadz, the B2B Contact Data Provider.
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM)
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) is the process of managing a product/service across its complete lifecycle including ideation, design, development, deployment, testing, rollout, and termination.
Example: Starbucks and Apple are some good examples of PLM.
Product Purchase Cycle
Product Purchase Cycle is a process in which a customer goes through when purchasing a product.
Example: Suppose, a customer has seen a bag on Amazon. He likes it and after giving a forethought, he finally purchases it. This entire process is a product purchase cycle.
Product Qualified Lead (PQL)
Product Qualified Lead (PQL) is a potential lead with a relatively higher likelihood of making a purchase, meeting predefined criteria, and having used benchmark products.
Example: A prospect that meets the criteria of an ideal customer profile.
Professional Employer Organization (PEO):-
Professional Employer Organization (PEO) refers to a firm that offers business/administrative services such as employee benefits, payroll, workers’ compensation, risk/safety management, recruiting, training, and development, to employers.
Example: ADP, Paychex, Justworks, or Insperity.
Profit Margin
Profit Margin is defined as the ratio of profitability that shows how much a company’s earnings. It is presented as either net income over revenues or net profit over sales. To calculate profit margin, divide your net income by revenues.
Example: Suppose, if your net income was Rs. 5,00,000, and your revenue was Rs. 20,00,000, your profit margin would be 25%.
Profitability
Profitability is the ability, potential, metric, degree, or relative efficiency of a business to obtain financial gain after the deduction of relevant expenses.
Example: Suppose, a customer stays with your company for 4 years and the annual profit from that customer is Rs.2 lakh. So, the profitability from that customer is Rs.8 lakh.
Proof of Concept (PoC)
Proof of Concept (PoC) is a demonstration, study, or prototype that attempts to prove the value and potential success of a business idea.
Example: During the product development, various trials are conducted to collect proof of concept before finalizing it.
Prospect
In the context of sales, a prospect refers to a potential customer who has an ideal customer profile.
Example: Any potential lead who meets the criteria of an ideal customer profile.
Prospecting
Prospecting is the process of searching for and finding potential buyers that they can move through the sales cycle. It is the term for leads or decision-makers who show interest in the product/service being offered.
Example: Cold calling, cold emailing, or social selling.
Protected Territory
Protected Territory refers to information such as first and last name, background, and possible needs researched for building rapport with the lead/prospect.
Example: First name of your potential customers.
Puppy Dog Closing
Puppy Dog Closing is a sales strategy for no-obligation customer usage of a product to try out while they make their purchase decision.
Example: Perfume Testers are usually given to the clients for puppy dog closing.
Purchase Order (PO)
Purchase Order (PO) means a document issued by a buyer to indicate services/products and corresponding costs intended to be purchased from the seller.
Example: A company usually asks for PO from the seller before making a hefty payment for a product or service.
Push Counter
Push Counter refers to a dashboard tracker used in the Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system that analyzes and checks how frequent closing an opportunity is pushed or postponed.
Example: HubSpot or Salesforce
-Q-
Qualified Lead
Qualified lead is an individual or organization that communicates with the company to enquire more about the product or service. There are two types of qualified leads: 1. Sales qualified lead 2. Marketing qualified lead.
Example: Let’s assume a person submits his email address for a newsletter while reading a blog on your website. So, that person is a qualified lead for you.
Qualifying Your Prospect
Qualifying your prospect is an act of receiving verbal confirmation from a potential customer that they are ready to make a purchase decision.
Example: A customer agrees to make the payment by the end of the day.
Quarter
Quarter is a fixed time period of three months in a company’s financial calendar wherein reporting earnings, paying dividends, comparing performance analysis, and forecasting is done.
Example: There are 4 quarters in a year such as Q1 for the first quarter, Q2 for the second quarter, Q3 for the third quarter, and Q4 for the fourth or last quarter.
Quota
Quota usually refers to a sales goal or a set amount of selling that a sales professional is expected to meet over a specific time period.
Example: A B2B company has set a revenue quota of Rs.70,000 for the month for every sales representative.
-R-
Ramp Up
Ramp Up refers to the condition in which a salesperson or team has achieved full productivity, the effort to achieve that state, and the period at which quota is accomplished. It is also known as “Ramp Rate” or “Ramp Up Time”.
Example: When a salesperson meets a monthly target in a week is referred to ramp up.
Rapport
Rapports are the common things (such as names) between a sales rep and a prospect.
Example: Maintaining a good rapport in an organization is very essential to grow.
Recruiter
Recruiter is an agency or a person whose specific purpose is to find, evaluate, hire, and onboard people as employees in an organization.
Example: Educare Solution, Global Hunt, or Employee Deal Consultants.
Referral
Referral is an act or technique of lead generation through a recommendation or referral given by a third party that shares information about a new prospect to produce sales leads.
Example: Company A referring the tool Mr. E by EasyLeadz to Company B.
Referral Appreciation Gesture
Referral Appreciation Gesture is an act of giving a thank you note to acknowledge your appreciation for getting a referral from a current customer.
Example: Mr. E by EasyLeadz gives free credits on referrals.
Relationship Business Management (RBM)
Relationship Business Management (RBM) refers to the method in which customer interactions from a transaction-based paradigm are transitioned to one of a long-term subscription.
Example: Sending out a thank you card to the customers when they make a purchase.
Reply Rate
Reply Rate is an important metric to measure the performance of email campaigns. It is the number of recipients who have responded to your email.
Example: Suppose, you sent an email to 4,000 people, and 2,800 responded, then the reply rate would be 70% (2,800 divided by 4,000).
Request for Information (RFI)
Request for Information (RFI) is a standard business document that aims to collect text-based information about the offerings and capabilities of business entities or vendors.
Example: Sending offerings of an organization.
Request for Proposal (RFP)
Request for Proposal (RFP) means a business document that requests the service providers or vendors to submit a proposal or bid during procurement.
Example: Sending offerings of an organization.
Request for Quotation (RFQ)
Request for Quotation (RFQ) is a business document asking suppliers or service providers to provide comprehensive quotes or pricing for the purchase of an item or the completion of a particular task.
Example: Sending Pricing Plans.
Request for Tender (RFT)
Request for Tender (RFT) is a process where suppliers or service providers are formally invited to submit a proposal for the procurement of a commodity, item, or service.
Example: RFT includes the requirements and expectations of a client.
Retargeting
Retargeting means a practice that serves paid ads to people who have visited your website earlier but failed to make a purchase. It is also called remarketing.
Example: Target a user who browses through your website, subscribes for the newsletter, but then forgets to return.
Retention Rate
Retention Rate refers to a term that indicates the rate of existing customers or the client’s retention percentage.
Example: Let’s assume Company A had 100 customers at the beginning of the period, ended the period with 100 customers, and added 20 customers over the period. Then, they would have a customer retention rate of 80 percent: [(100-20)/100]*100 = 80 %.
Return on Investment (ROI)
Return on Investment (ROI) is a metric or percentage calculated by dividing the return (benefit) by the cost of investment, indicating the profitability of an investment.
Example: Suppose a businessman invested 2 lakhs into his new venture and that venture generated 4 lakhs in revenue. Then the ROI would be 200%.
Revenue
Revenue refers to the amount of money that a business generates during a given time period such as a month, a quarter, or a year. It is also called sales.
Example: Total sales made by a company in a period of time.
Ride-Along
Ride-along is a percentage of customers that are retained by the company.
Example: Customer retention rate of a company.
Right of First Refusal (ROFR or RFR)
Right of First Refusal (ROFR or RFR) is a term for the contractual right granted to a holder allowing the performance of particular business transactions with an entity before they are offered to third parties.
Example: A real estate owner offers a potential buyer to purchase his property at a fixed price before offering it to other buyers.
Rule of Reciprocity
Rule of Reciprocity is a sociological rule that motivates a person to treat others positively with the expectation of being treated in the same way.
Example: Suppose a random person helps you when your car breaks down on the road and changes your tire for you. Then, in the future, you will also help that person, if required, without giving a second thought.
-S-
SaaS
SaaS – an acronym for Software as a Service.
Example: EasyLeadz, MailChimp, Hubspot, Dropbox, or Slack.
Sales Acceleration
Sales Acceleration refers to the practice of using tools and technologies for speeding up the sales processes that help sales professionals boost their productivity and efficiency.
Example: CRM software, Business Intelligence (BI) software, Email tracking tools, or Digital adoption platforms.
Sales Automation
Sales Automation is the process of simplifying, speeding up, or streamlining the entire sales process using the software.
Example: EasyLeadz, HubSpot, Zapier, MailChimp, or Prospect.io
Sales Calls
Sales Calls are the phone calls that a sales rep makes to a potential lead to generate business.
Example: Calling up the signed-up users and arranging the demo for them.
Sales Champion
Sales Champion is a prospect who deeply understands and likes your product and has the influence and authority of advocating its adoption and success.
Example: Founders of small-sized startups.
Sales Coaching
Sales Coaching is the process of helping sales representatives to improve their performance, efficiency, and impact through the development of new skills.
Example: Pipeline reviews, team meetings, or deal reviews.
Sales Cycle
Sales Cycle is a repeating process that a company undergoes characterized by a predictable sequence of stages for selling its products and services to customers.
Example: Firstly, a sales representative will look for the prospects, and then prepare the pitch to approach the prospect. After this, the sales rep will present his product and also handle objections to close the deal. After closing the deal, he will take follow-ups for the feedback, reviews, or generating referrals.
Sales Demo
Sales Demo refers to the process of presenting the functions and value of a product/service with the goal of leading the audience towards a purchase.
Example: A demo of any product or service with the aim of selling it.
Sales Development Representative (SDR)
Sales Development Representative (SDR) is a sales specialist assigned to find new prospects, establish foundational relationships, and refresh the sales pipelines with new leads. It is also known as Business Development Representative (BDR).
Example: A SDR jobs include finding prospects and cold-calling them.
Sales Director
Sales Director is a senior-level executive tasked to oversee the sales operations by leading strategy, plans, and execution, supervising, and ensuring continuous sales growth.
Example: Mr. John Paulraj is the Sales Director at Zoho Corporation.
Sales Enablement
Sales Enablement is a strategic part of the sales process that provides a company’s sales reps with training, tools, and technology to improve their customer engagement.
Example: Seismic, Highspot, Showpad, and HubSpot.
Sales Engineer
Sales Engineer is responsible for translating technical terms to layman to answer technical questions and conducting product demos for qualified leads.
Example: Most IT companies have Sales Engineers.
Sales Funnel
A sales funnel is a path that indicates where your prospect is in their buying journey, whether they have just become aware of your product/service or they are ready to become a paying customer.
Example: What Is A Sales Funnel? Importance, Stages, And How To Build One.
Sales Kickoff
Sales Kickoff is a major annual event for celebrating the previous year’s key achievements and setting company goals, and new revenue to deliver continued high performance for the coming year.
Sales Lead
Sales Lead is a prospect who has shown interest in the company’s product/service and given their contact information to the company.
Example: Any potential lead.
Sales Manager
Sales Manager is an executive assigned to set goals, meet targets, formulate plans, develop salespeople and designate tasks.
Example: Leader of a sales department.
Sales Methodology
Sales Methodology is the framework that shows how your sales professionals are doing in each step during the sales process.
Example: Sales Funnel
Sales Operations
Sales Operations is a collection aimed at achieving organizational goals.
Example: Sales revenue, market coverage, and growth through strategic implementations.
Sales Partnerships
Sales Partnerships refer to a formal collaboration between individuals and organizations for mutual benefit to accelerate the sales performance of a product or service.
Example: Company A collaborating with Company B to accelerate their sales.
Sales Pipeline
Sales pipeline reveals the number of expected closures for a given period. It shows the status of the sales prospect in the sales process.
Example: Suppose a sales rep has 4 expected closures for a current week, then it means there are 4 leads in his sales pipeline that will help them to reach his target.
Sales Pipeline Coverage
Sales Pipeline Coverage is a metric measuring whether current businesses present meet expected goals.
Example: Suppose a sales rep has 4 expected closures for a current week, then it means there are 4 leads in his sales pipeline that will help them to reach his target.
Sales Process
Sales Process is a series of strategic steps to drive sales growth.
Example: Selling of any product.
Sales Productivity
Sales Productivity is a metric indicating a sales unit’s efficiency at closing sales and generating revenue. It is based on sales volume, payroll expenses, personnel activity level, and others.
Example: A salesperson who makes 100 calls in a day to qualified leads refers to sales productivity.
Sales Prospect
Sales prospect is a potential customer with the buying authority, financial capacity, and willingness to buy the product or service.
Example: A potential lead who meets the criteria of Ideal Customer Profile.
Sales Prospecting
Sales Prospecting is the process of using networking, cold calling, and advertising, to find and qualify potential buyers.
Example: Finding a prospect who meets the criteria of Ideal Customer Profile.
Sales Qualified Lead (SQL)
Sales Qualified Lead (SQL) is a marketing qualified lead who has shown higher interest in making a purchase.
Example: A Potential Buyer.
Sales Related Activities
Sales Related Activities are the vital sales stats wherein a demonstration of a product/service for a prospect is done, with the aim of making a sale.
Example: Cold Outreach, Prospecting, or Demos.
Sales Roles
Sales roles are the representatives of the sales department that ensure a smooth sales process.
Example: Inside Sales Rep, Sales Development Rep, Sales Engineer, etc.
Sales Sequence
Sales Sequence is a sequence of activities upon which the sales team attracts a prospect or an account.
Example: Sales Funnel
Sales Territory
Sales Territory refers to the area of focus of sales reps wherein they are to make sales.
Example: A sales rep assigned to focus on urban areas for selling the company’s products.
Sales Training
Sales Training is a process of enhancing the skills, mindset, and behavior of sales representatives to enhance the efficiency of their sales performance.
Example: Workshops, seminars, or training.
Salesforce Administrator
Salesforce Administrator is usually a team leader or manager assigned to maintain high employee productivity and engagement.
Example: A person assigned to operate and maintain the Salesforce CRM.
Sandbagging
Sandbagging refers to the act of postponing closing active deals after you hit your quota for the month. to keep extra sales under process, in order to ensure that you will be able to hit numbers in the next month.
Example: Suppose, a salesperson has reached his quota for the current month by making 10 sales and still there are 5 more active deals in his pipeline. Now, he will close those 5 deals in the next month to meet his next month’s quota timely.
Sandler Training
Sandler training is training on sales, management, and leadership provided by an organization to professionals worldwide.
Example: Every organization provides Sandler training to its sales professionals from time to time.
Schedules and Habits
Schedules and Habits are the regular schedules and habits of a sales rep that states the number of demos and sales made.
Example: Scheduled Appointments
Scraping
Scraping means the extraction of large data from websites.
Example: Academy Scraper is a tool for scraping data.
Segmentation
Segmentation is a process of separating large markets into different segments according to demographics to build respective strategies and engage consumers in each segment.
Example: To run a market campaign, marketers usually segments the locations as per the market requirements.
Selling the Sizzle
Selling the Sizzle is a strategy or a technique of selling the benefits of a product rather than its features.
Example: Companies who sell smartphones usually use this technique.
Selling, General, And Administrative (SG&A)
Selling, General, And Administrative (SG&A) are the expenses not linked with the production of products or services, these are often listed in a company’s income statement under operating costs.
Example: Rent and utility costs, employee benefits, and marketing expenditure.
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) / Domain Keys Identified Mail (DKIM)
Sender Policy Framework (SPF)/Domain Keys Identified Mail (DKIM) is an online security process that verifies and prevents email fraud, phishing, spam, and spoofing.
Service Level Agreement (SLA)
Service Level Agreement (SLA) refers to the contract between a service provider and a consumer.
Serviceable Available Market (SAM)
Serviceable Available Market (SAM) refers to a portion of the Total Addressable Market (TAM) targeted by a company based on its current capabilities.
Serviceable Obtainable Market (SOM)
Serviceable Obtainable Market (SOM) is a part of the Serviceable Available Market (SAM) that a company can realistically achieve in the short term.
Share Purchase Agreement (SPA)
SPA is a legal contract between the company, its shareholders, and investors that finalize the terms and conditions for the purchase and sale of shares. It is also known as the Share Sale Agreement.
Shareholders’ Agreement (SHA)
Shareholders’ Agreement (SHA) is a contract among the shareholders of a company that authorizes the standards for the company’s operations and stipulates the rights and obligations of shareholders.
Side Selling
Side Selling is the practice of selling complementary products or services to a customer who uses a competitor for your main product.
Example: Selling of hair conditioners along with shampoos.
Signaling
Signaling is a process in which a consumer shows a willingness to purchase your product or service by signing up or asking questions about your solutions.
Example: A person signing up for Mr. E tool is a signal for the sales rep of EasyLeadz.
Signup Conversion Rate
Signup Conversion Rate refers to the percentage of website visitors that convert to registered users. It is calculated by dividing the total number of registrants by the total number of landing page visitors.
Example: Suppose, you have 400 website visitors and among them, 60 signed up on it. So, the signup conversion rate would be 15%.
Signup-to-Paying Conversion Rate
Signup-to-Paying Conversion Rate is a percentage of prospects that become paying customers who converted their free accounts into paying accounts.
Example: Suppose, you have 100 signed-up users and among them, 10 become paid users. So, the signup-to-paying conversion rate would be 10%.
Single Sign-On (SSO)
Single Sign-On (SSO) is a technique considered safer in both cybersecurity and enterprise permissions as it allows access to multiple but independent software systems using a single ID and password.
Small and Mid-size Business
Small & Mid-Size Business (SMB) refers to a business organization that has a limited number of employees, usually, a small business has less than 100 employees while a mid-sized business has 100-999 workers.
Example: Medical stores, Bakeries, or Grocery stores.
Smarketing
Smarketing is an act of aligning the Sales and Marketing operations of a business to increase revenues through an integrated shared strategy.
Example: Marketing requires delivering more quality leads, whereas sales teams require to close qualified leads.
Smile and Dial
Smile and Dial is a cold-calling but with a positive and bright tone of voice.
Social Selling
Social Selling is an act of using social media platforms to offer value by answering the prospect’s questions and providing relevant help until they buy.
Example: Selling via LinkedIn.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a software distribution model in which customers access and utilize the software on the internet under a subscription agreement.
Example: EasyLeadz, Dropbox, MailChimp, etc.
Solution
Solution is a set of useful ideas, technologies, and services, that effectively helps a business to achieve its goals amidst challenges.
Example: Mr. E by EasyLeadz is a solution for B2B companies to get the contact details of decision-makers with a single click.
Solution Selling
Solution Selling is a sales approach in a B2B environment wherein a sales rep analyzes the customer’s problems and proposes a solution using the company’s products or services.
Example: A B2B company providing its prospects a solution of getting the contact details of top management with ease.
Sound Bite
Sound Bite refers to a set of words or phrases used by a salesperson to overcome a customer’s objections.
Example: “You are not going to regret purchasing this software”.
Spiff
Spiff is an instant financial bonus, paid vacation, or non-cash prize for achieving a milestone. It is a quickly awarded incentive.
SPIN Selling
SPIN – an acronym that stands for Situation, Problem, Implication, and Need-payoff. These are the four types of questions a sales rep must ask a potential lead to form a customer-centric paradigm and increase the closing rate.
Stage
Stage is a phase of the sales pipeline that indicates a particular step in the sales process.
Example: Top of the Sales Funnel, Middle of the Sales Funnel, and Bottom of the Sales Funnel
Stakeholder
Stakeholder is a person or an organization who shows interest in buying the shares of a company.
Straight Commission
Straight-Commission means working only on a commission basis.
Strategic Investment/Smart Money/Corporate Venture Capital (CVC)
Strategic Investment/Smart Money/Corporate Venture Capital (CVC) refers to investments made by corporations, angel investors, and venture capitalists in businesses and startups.
Structured Data
Structured Data refers to highly organized information added into, managed, and searched for in a database effortlessly.
System of Record (SOR)
System of Record (SOR) is a management system and information storage that acts as an authoritative source for particular data items in systems where multiple sources of the same items exist to protect data integrity.
-T-
Target/Targeting
Target/Targeting refers to the group of prospects in which a company plans to market its products or services.
Example: The company that deals in kids’ toys, targets them or their parents for selling its products.
Temperature Questions
Temperature Questions refer to the set of questions asked by a salesperson to identify the prospective customer’s position in the buy-line.
Example: “When will the need arise?” is a temperature question.
Template
Template is a generic but preformatted document consisting of a set of standard features that are used to create a new document of the same type faster and easier.
Example: Onboarding Templates, Offering Templates, or Features Templates.
Tenor
Tenor is the amount of time left to fully pay a loan until the financial contract defining its terms and conditions expires.
Example: If you take a home loan, that needs to be paid back in 10 years then this period of 10 years is referred to us as a tenor.
Territory
Territory is a term for questions that are asked to gauge the level of the potential lead in consideration of the buy-line.
Example: “How many leads do you require in a month?” is a territory question.
Territory Management
Territory Management is a term for the area in which the salesperson is assigned to focus on getting customers.
Example: Suppose Company A assigned a rural area to his sales reps for getting clients.
Time Bandits
Time Bandits refers to the geographical area that is properly worked on by an assigned salesperson with the aim of increasing monetary profit from that location.
Example: Sales rep transferring to the city with the aim of increasing profits.
Time Kills All Deals
Time Kills All Deals is a phrase showing how the sales deal should be made within the shortest time possible because it is less likely to happen as time passes.
Example: Imagine you run a marketing campaign, and you get some inquiries. If you delay in contacting them then you may lose quality leads.
Tire-Kicker
Tire-Kicker is a prospect that has neither the real intention nor the ability to purchase but might be genuinely interested in the product.
Example: A prospect who inquires everything about the product but at the end denies to purchase.
Top-Level Domain (TDL)
Top-Level Domain (TDL) is the highest-ranking domain in the Domain Name System of the Internet (DNSI).
Example: The domain name extensions .info, .com, .net, and .org.
Top of the Funnel (TOFU)
Top of the Funnel (TOFU) is the first stage in the sales funnel (buying process) where you attract your prospects through promotional or advertising activities.
Example: When a prospect starts inquiring about your product as a result of a marketing campaign.
Total Addressable Market (TAM)
Total Addressable Market (TAM) is the largest possible revenue opportunity for a specific company, organization, or business.
Example: Number of people who signed up on EasyLeadz for Mr. E tool.
Total Available Market
Total Available Market is the total revenue potential for a specific product or service while also considering its market input in the future.
Example: For a startup company that deals in B2B products, the total available market is all the B2B companies.
Total Value to Paid In (TVPI)
Total Value to Paid In (TVPI) is a metric used to measure fund performance.
Example: The ratio of distributed and undistributed investments in a fund to the amount of invested capital.
Touches
Touches or touchpoints refer to the milestones or the points of contact used to measure the marketing effort needed to make a qualified lead from a prospect.
Example: Before purchase, after purchase, company blog, customer reviews, or social media are some customer touchpoints.
Tranches
Tranches refer to slices or portions of debt released consecutively within a given time period.
Example: Bonds or Loans can be divided into tranches.
Triggers
Triggers are a set of signals that signify the chance to make a sale.
Example: Suppose, a prospect signs up for a registration form, then it would be a trigger for a sales rep.
Turn-Over Rate
Turn-Over Rate is defined as the amount of time that is provided to a new sales rep before they are expected to make profits.
Example: Usually one month for the new sales reps.
-U-
Unicorn
Unicorn is a startup company valued at more than a billion-dollar.
Example: Inmobi, Flipkart, Zomato, Swiggy, Droom, Meesho, and many more.
Unique Selling Point / Proposition (USP)
Unique Selling Point / Proposition (USP) is a marketing concept that helps companies define their unique advantage (price, quality, services, or features) over their competitors and make them stand out with their offer.
Example: The USP of EasyLeadz is to provide 100% accuracy assurance on their contacts.
Unit Economics
Unit Economics refers to the application of economic principles as they impact an entity such as a customer or a business.
Example: If you consider a unit as “one customer”, then the unit economics for that customer is the ratio of LTV (Customer Lifetime Value) and CAC (Customer Acquisition Cost).
Up And To The Right
Up And To The Right is a description of when one makes a good sales pitch or business proposal.
Example: Up And To The Right describes the growth of an organization.
Upselling
Upselling is a selling technique where a seller introduces a more profitable or an up-grade version of the product to a buyer that he/she initially bought.
Example: Suppose, if a salesperson upgrades your broadband plan to a much faster than the initial one.
User
User refers to a person who uses a product or service, whether online or offline.
Example: An iPhone user.
User Experience (UX)
User Experience (UX) UX consists of everything that covers the user’s interaction with any product, service, brand, business, or company.
Example: In digital marketing, a good UX helps to drive excellent CTA performance.
User-Generated Content (UGC)
User-Generated Content (UGC) refers to the content created by users. Brands can highly benefit by encouraging their users to create content as people are more likely to trust what their fellow customers say about a brand.
Example: Social media posts, blog posts, opinions, or online reviews.
User Interface (UI)
User Interface (UI) refers to all the elements of an app, software, website, or device that allow users to interact with it.
Example: Menus, Hyperlinks, and Buttons of websites to navigate a web page.
-V-
Value Proposition
Value proposition is a benefit of a product or company intended to make it more attractive to potential customers and stand out against the competition.
Example: The value proposition of Uber company is “The Smartest Way to Get Around”.
Value Statement
Value statement is a marketing message from the company that informs customers about the advantages as to why they should purchase its product or service.
Example: The value statement of EasyLeadz is “Find Phone Numbers of top management In One Click”.
Value Triangle
Value triangle is a concept in sales and marketing that describes the inter-relationships among three main factors: cost, quality, and speed; to help customers in determining the value of a product or service.
Example: A customer seeks quality, speed, and an affordable cost for a product while purchasing. This makes a value triangle of that product.
Vertical
Vertical refers to a marketing strategy where a company only targets a particular group of customers such as a particular sector, profession, or industry.
Example: Manufacturers of car engines cater only to the companies that manufacture cars.
Virtual Machine (VM)
Virtual machine is a software-driven solution that acts like an actual computer, equipped with a dedicated system and an operating system.
Example: Java Virtual Machine
Vital Sales Stats
Vital sales stats are the most important sales numbers to track for you to be successful as a sales executive.
Example: Vital sales stats help in discovering the growth of a salesperson.
-W-
Warm Call
Warm call is the process of calling or visiting a prospect with whom the sales representative has had a prior contact such as during a company event or a party.
Example: Imagine you meet a prospect at a company event and they ask you to call them so that you can set up an appointment, that would be an extremely warm call for you.
Warm E-mail
Warm e-mail is the process of emailing a potential client with whom the sales representative has had contact before sending the first e-mail.
Example: Suppose you meet your ex-colleague at a corporate event and he asks you to email him so that you can schedule a demo for your product, that would be a warm email.
Warrant
Warrant is the right of the holder to purchase shares from the issuing company within a given time period.
Example: If the stock warrant is for 1,00 shares of stock and is sold at Rs.1000, this means the price for the warrant is Rs.1000 per share.
Weighted Pipeline
Weighted pipeline is a detailed version of a sales pipeline, in which each point has a value based on which stage they are in the sales process.
Example: Suppose, if the entire amount of a deal is Rs.50,000, and you have weighted selected, then it will show at 50% of the deal which is Rs.25,000.
Whale (or White Whale)
Whale or a white whale is a business prospect who has the potential to bring considerable revenue to the company.
Example: Big companies whose requirements align with your product/service.
White Hat
White hat refers to an excellent or lawful behavior, but can also pertain to any illegal activity that has been permitted by the government for protective purposes.
Example: Many companies pay for White hat hackers to test their computer systems and identify vulnerabilities.
White Label
White Label refers to a product or service that can be purchased by a company and legally re-sold and marketed under the company’s own trademark.
Example: Trimmers, Glasses, Bags, or Coffee products.
WIIFM
WIIFM is an acronym that stands for “What’s In It For Me”. This is the first question that your email recipients (prospects) ask themselves before opening your email, or accepting your offer.
Example: To make a sale, a pitch should answer WIIFM for its clients.
Wireframes
Wireframes mean rough representations of any service or product that indicate how either is structured and organized.
Example: Search Results for e-commerce website, Loan app screens, or Hand-drawn wireframe.
-X-
Xenocurrency
Xenocurrency or “foreign currency” refers to a currency that is being traded (deposited or exchanged) in a market outside its country of origin.
Example: INR (Indian rupee) exchanged in the US.
X-Efficiency
X-efficiency is defined as the ability of a company to make the maximum output from its input in a given market.
Example: Suppose a company may be 0.80 x-efficient, which means it is operating at 80% of its optimal efficiency.
X-Inefficiency
X-inefficiency is defined as the inability of a company to get the maximum output from its input due to the lack of competitive pressure.
Example: Let’s say if an organization does not have supervision of workers then the productivity will fall as workers ‘take it easy’. So this lack of management control is an x-inefficiency of that organization.
-Y-
Year-to-Date Net Income
Year-to-date net income is the after-tax earnings (profit) that a company generated from the beginning of the fiscal year up to the present reporting date.
Example: The year-to-date net income on March 31, 2022, for the fiscal year 2021-22 is the net income from April 1, 2022 to March 31, 2022.
-Z-
Zeroed Out
Zeroed out is when sales representatives earn enough commission to make their draw balance equal to zero. They can start earning their commission again once their draw account has been zeroed out.
Example: In sales, there is usually a cap on commission, any amount above that is zeroed out.
B2b Sales
Marketing
Marketing Terms
SaaS Sales
Sales
Sales Glossary
Sales Terminology
Sales Terms